CrowdStrike Teams with the MITRE Engenuity Center for Threat-Informed Defense in Development of TRAM II
- As a Research Partner for the MITRE Engenuity Center for Threat-Informed Defense, CrowdStrike was involved in the development of a new version of the Threat Report ATT&CK Mapper (TRAM)
- CrowdStrike provided expertise to the TRAM II project as a leader in external threat intelligence and world-class AI
- To counter the cybersecurity skills gap and accelerate industry adoption of the MITRE ATT&CK® framework, the TRAM II project aims to improve the speed and accuracy of mapping new threat reports to the MITRE ATT&CK framework through automation
The MITRE ATT&CK framework provides the cybersecurity industry with a common language for describing adversary behaviors, making it invaluable for organizations building or operating cyber defenses, as well as advancing research across the threat landscape.
Mapping threat intelligence reports to the ATT&CK framework is difficult, error-prone, time-consuming and heavily reliant on specialized expertise. There is a shortage of expert-level ATT&CK annotators, so even organizations with the resources to hire these experts struggle to find them and struggle to find individuals qualified to conduct training in ATT&CK annotation. Annotation is an art as much as it is a science: Expert annotators can disagree on the appropriate mapping of the same text. These disagreements can stem from ambiguities in the text being annotated, extra-textual connotations of certain words or even an individual annotator’s history with the application of a particular ATT&CK tactic or technique.
The goal of the Threat Report ATT&CK Mapper – otherwise referred to as the TRAM project – is to integrate ATT&CK more easily and consistently into security implementations by streamlining how the content of threat intelligence reports are mapped to ATT&CK.
TRAM aims to automate this process as much as possible, reducing the burden on expert annotators and improving consistency of mapping across organizations. Doing so will reduce the time and monetary costs of adopting the ATT&CK framework. The TRAM project is a platform developed by the Center for Threat Informed Defense for the purpose of reducing the cost and increasing the effectiveness of integrating ATT&CK into security implementations. TRAM enables researchers to train and refine machine learning models capable of identifying ATT&CK techniques in threat intelligence reports. TRAM also provides the ability for threat analysts to train machine learning models and validate results.
CrowdStrike sees this project as generating significant value for both producers and consumers of threat intelligence. As a threat intelligence producer, the CrowdStrike Intelligence team has annotated its reports with ATT&CK tactics and techniques for over a year to streamline operationalization of its threat intelligence. However, doing so — especially for multiple versions of ATT&CK — is a significant ongoing investment for our analysts. We believe TRAM will make it significantly easier for threat intelligence authors to distribute their reports with granular ATT&CK annotations, and organizations consuming threat intelligence will be able to use TRAM to maintain a consistent experience for their own analysts, even if not all of their providers offer granular ATT&CK annotations.
TRAM II is the second iteration of the TRAM project. For TRAM II, the team sought to leverage the latest advances in text classification and natural language processing (NLP) to automate the classification of tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) in cyber threat intelligence reports.
Project deliverables were:
- New machine learning architecture
- Data annotation tools
- Improved training data
- Alternate data sources
- Retraining capability
Technical Details of Implementation
While TRAM I used sentence-level annotation, TRAM II required a shift toward phrase-level annotation. This is a more reusable and scalable approach: Phrase-level annotation can be automatically re-interpreted at the sentence level if needed for a model, but the reverse is not possible. Feedly was used to collect new Cyber Threat Analysis (CTI) reports describing malware, ransomware, software, threat actors and specific TTPs. The 150 new CTI reports were then fed into the MITRE Annotation Toolkit (MAT) for analysis. In addition, 50 ATT&CK technique labels were imported into MAT. This resulted in over 4,000 technique-labeled sentences, constituting a refreshed data set aligned with ATT&CK v.13, demonstrating the speed and scalability that this technology offers in advancing and updating the industry’s understanding of ever-changing attack patterns.
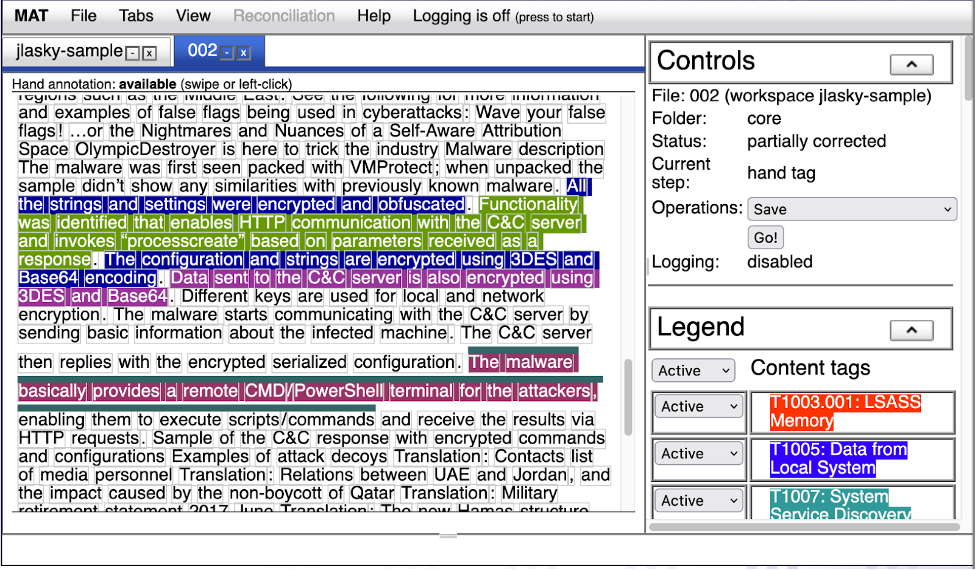
Figure 1. MAT Data Annotation Tool (Source: Center for Threat-Informed Defense TRAM II project) (click to enlarge)
The data was then reformatted for future large language model (LLM) efforts.
The TRAM II team considered different machine learning models including BERT and GPT-2 before selecting the fine-tuned SciBERT LLM to meet target prediction accuracy levels. SciBERT LLM is an open source LLM based on BERT (which is designed primarily to predict missing words in text samples) pre-trained on scientific text. Testing results showed that SciBERT can learn the distinction between different ATT&CK techniques.
CrowdStrike’s TRAM II Involvement Reflects Ongoing Commitment to Cybersecurity Innovation
CrowdStrike’s commitment to cybersecurity extends beyond the best-in-class protection of the CrowdStrike Falcon® platform.
CrowdStrike researchers work around the clock to ensure we remain a step ahead of the most sophisticated adversaries. Publicly publishing many of our findings advances defenses worldwide against newly discovered tactics and malware, and also helps drive development of testing and evaluation tools that cover the latest cybersecurity threats.
Our industry research involvement extends to being a Research Partner in the MITRE Engenuity Center for Threat-Informed Defense, supporting the Center’s mission to advance the state of the art and the state of the practice in threat-informed defense globally. Participation in the TRAM II project is CrowdStrike’s latest contribution to the Center’s cybersecurity R&D efforts.
CrowdStrike is an industry leader in external threat intelligence and knowledge of adversarial tradecraft. We are also a global leader in artificial intelligence and machine learning, with the Falcon platform including AI-powered indicators of attack (IOAs) and Charlotte AI, the engine powering our portfolio of generative AI capabilities across the platform utilizing CrowdStrike’s high-fidelity data advantage. CrowdStrike researchers participating in the project provided expertise to help guide TRAM II to a successful completion.
Additional Resources
- Join us at Fal.Con 2023, the can’t-miss cybersecurity experience of the year. Register now and meet us in Las Vegas, Sept. 18-21!
- Learn how you can stop cloud breaches with CrowdStrike unified cloud security for multi-cloud and hybrid environments — all in one lightweight platform.
- Read about adversaries tracked by CrowdStrike in the CrowdStrike 2023 Global Threat report.
- Test CrowdStrike next-gen AV for yourself. Start your free trial of Falcon Prevent™ today.