Compromised NPM Package Used in Supply Chain Attack: CrowdStrike Falcon® Customers Protected

- Popular NPM package with over 7 million weekly downloads was compromised and used to distribute cryptocurrency miners and password stealers
- NPM library is used by developers to publish and download node.js projects
- Attackers hijacked the package developer’s account for hours, with an unknown number of users affected
- Measures are taken to ensure systems residing in Russia, Ukraine, Belarus or Kazakhstan are not impacted
- CISA issued a public US-CERT Alert on Oct. 22, 2021, urging users and administrators to update to patched versions
- CrowdStrike uses automated detection and protection capabilities to proactively protect clients from threats delivered via the compromised NPM package
On Friday, Oct. 22, 2021, a popular NPM package was compromised. This open source NPM repository is used by developers to publish and download node.js projects, and an account housing a node.js package — with more than 7 million weekly downloads — was hijacked. Attackers uploaded tainted versions of the popular node.js package (ua-parser-js) in a supply chain attack that could have had devastating consequences if not discovered in time. The CrowdStrike Falcon® platform proactively protects customers against exploitation of this compromise.
Supply Chain Attacks on the Rise
Supply chain attacks are on the rise, with adversaries shifting their attacks upstream by infecting open source components that are distributed downstream and installed potentially millions of times. Malicious code was discovered in this popular JavaScript library, leading to malware being deployed in an attempt to mine cryptocurrency or harvest credentials from affected systems.
On Oct. 22, the same day the author’s account was compromised and used to push the tainted libraries, CrowdStrike Falcon® automatically detected and prevented malware delivered through the compromised packages, protecting customers.
Once the victim installs the compromised node package, the package will perform a check to determine which operating system it is executing on, and based on that check, either a .bat or .sh file will run. These files will download and execute XMRig on both Windows and Linux, and SCULLY SPIDER’s DanaBot loader on Windows.
Recent supply chain attacks have also involved malicious open-source JavaScript libraries or malicious Python modules used to deliver cryptocurrency miners. These attempts involved typosquatting package names by using misspelled names of legitimate packages that could be included in projects by mistake, whereas the latest incident with the ua-parser-js library involved compromising the author’s account associated with the library.
In the recent node.js incident, after hijacking the developer account, attackers modified the library and pushed three ua-parser-js versions: 0.7.29, 0.8.0 and 1.0.0. After several hours where the tainted packages were available for download, the legitimate developer was alerted and published new clean versions of the library: versions 0.7.30, 0.8.1 and 1.0.1, respectively.
Supply chain attacks are particularly concerning, especially those affecting software supply chains, as they rely on off-the-shelf components and open-source code from vendors or repositories. With more dependencies between software projects and applications, the number of victims potentially impacted by a compromised component can increase exponentially.
CrowdStrike Protection From Tainted NPM Package
CrowdStrike Falcon®’s automated detection and protection capabilities and the power of the cloud protect customers from sophisticated adversaries and commodity malware, including this supply chain attack involving compromised node.js packages, and other attacks that deliver malware through tainted open-source packages. CrowdStrike Falcon® uses behavior-based detection of indicators of attack (IOAs) to identify and block malware delivered through the tainted library and incorporates intelligence derived by continuously monitoring tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) related to over 160 threat actors and numerous unnamed groups.
A payload deployed by the tainted package involves executing a cryptocurrency miner with the filename “jsextension.exe” downloaded in the same “dynamictemplate\node_modeules\ua-parser-js” location as the tainted package. Falcon immediately identifies the malicious behavior associated with cryptocurrency miners and immediately blocks the process from executing, protecting the endpoint.
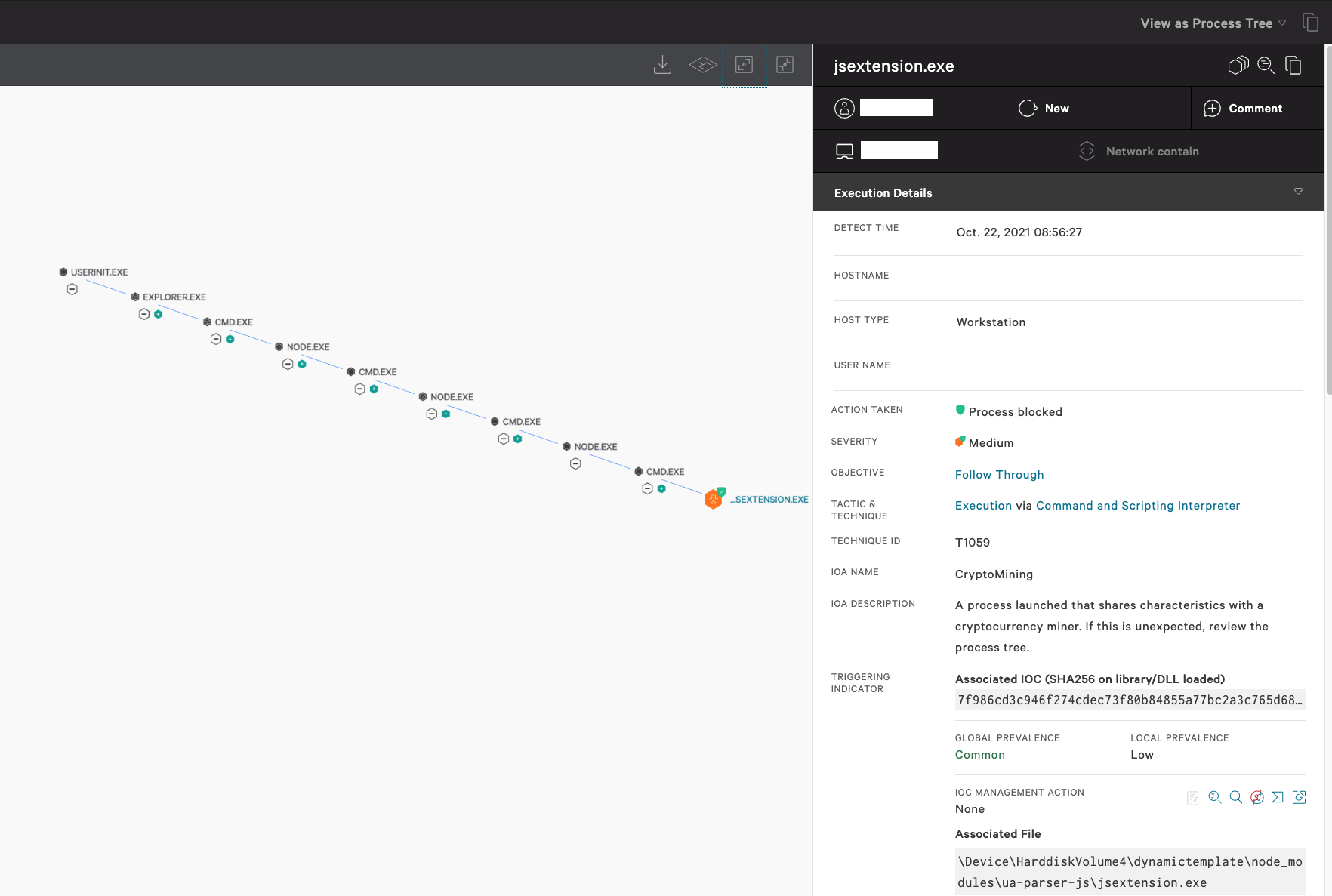
Figure 1. Falcon detects and prevents download and execution of cryptocurrency miner (Click to enlarge)
As seen in the image below, the malicious node.js package attempts to use a legitimate Windows certificate utility, certutil.exe, to download a payload from a remote location, specifically a command and control server. Leveraging behavior-based detection capabilities, Falcon automatically detected and blocked this tactic as malicious, warning that this activity is rarely used benignly.
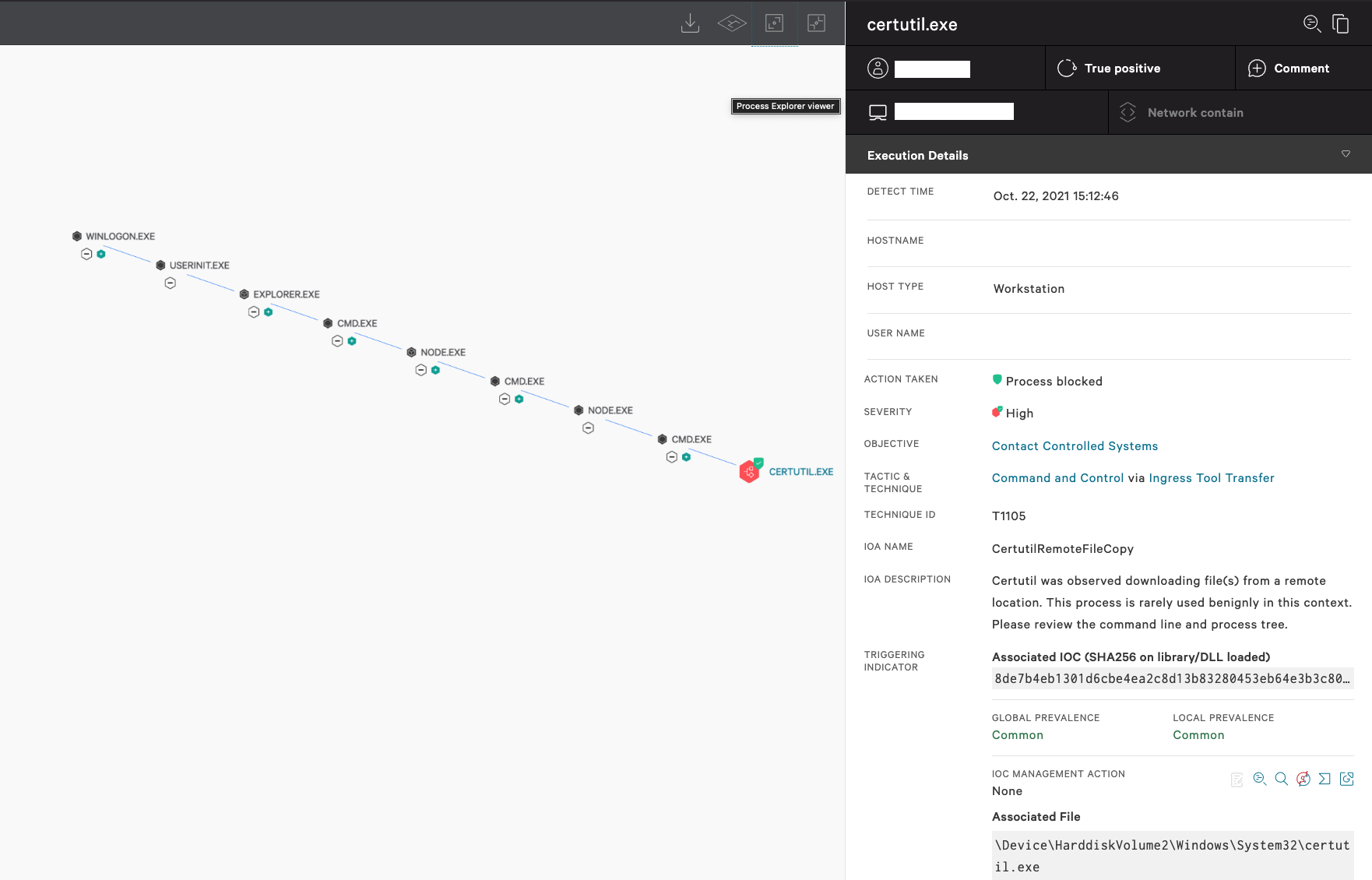
Figure 2. Falcon detects and prevents certutil.exe abuse from downloading a malicious payload from a remote location (Click to enlarge)
Below, another behavior automatically detected and blocked by Falcon involves the abuse of a command-line utility in Microsoft Windows (regsvr32.exe), used for registering and unregistering DLLs in the OS registry, to download a malicious “create.dll” file from a remote location. In this case, the file was identified as the DanaBot trojan, known to be operated by the SCULLY SPIDER eCrime group.
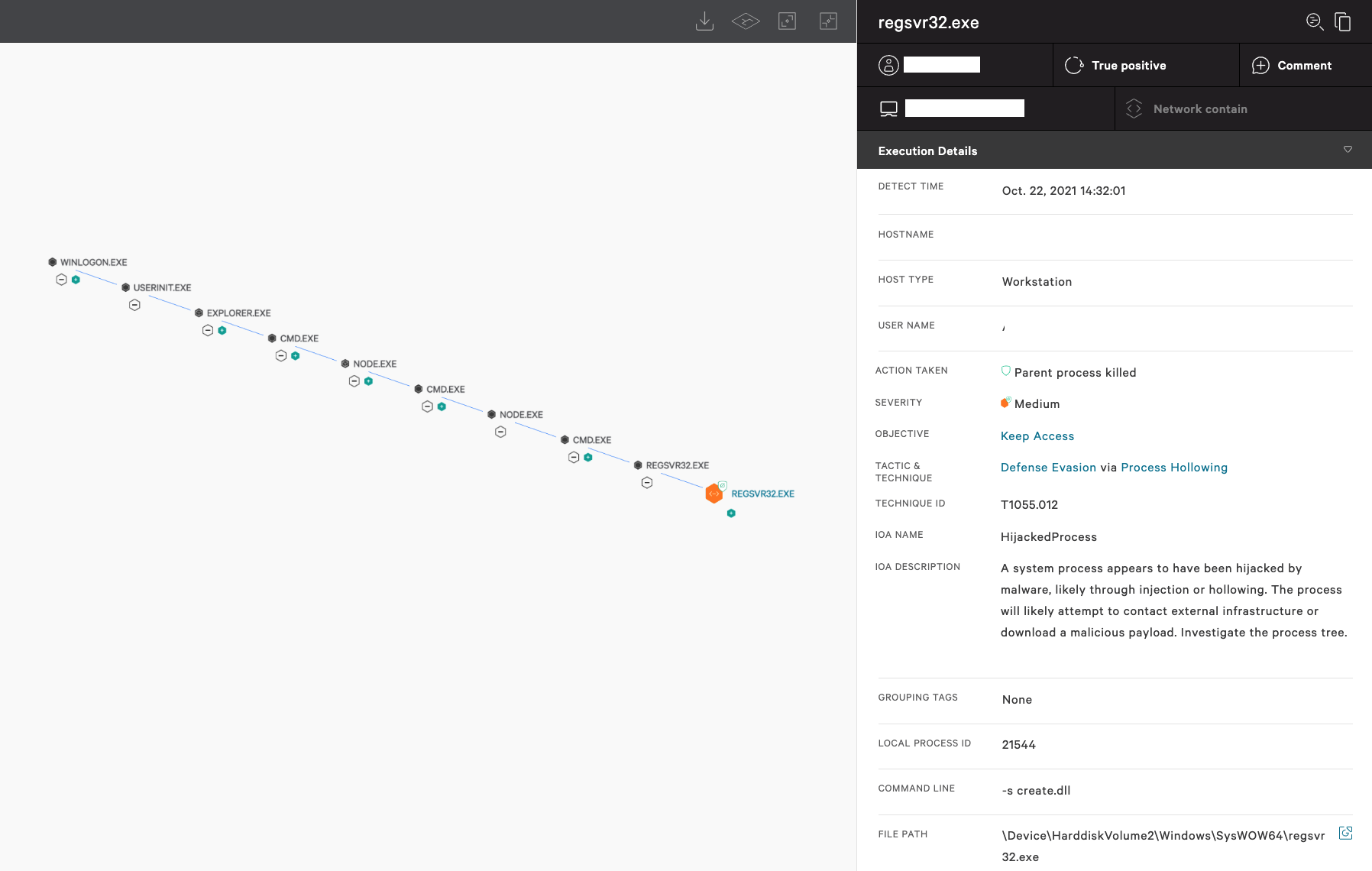
Figure 3. Falcon detects and prevents regsvr32.exe from downloading DanaBot trojan DLL (Click to enlarge)
Process injection is a common tactic used by attackers to execute potentially malicious files or processes in the context of legitimate or benign ones. Using IOAs, Falcon automatically detects and prevents this malicious behavior, killing the abused process.
Supply chain attacks pose significant risks to organizations, as poisoned open source repositories can potentially have a devastating impact. The CrowdStrike Security Cloud processes approximately 1 trillion of events per day to identify potential IOAs and makes more than 150 million IOA decisions every minute to automatically detect and protect against threats from sophisticated adversaries and commodity malware, such as cryptocurrency miners and password stealers. Protecting customers against adversaries like SCULLY SPIDER is what the CrowdStrike Falcon® platform does every day.
Note: More detailed intelligence and technical information about the eCrime adversary SCULLY SPIDER and DanaBot are available to CrowdStrike customers through the Falcon console.
Independent third-party validation from leading testing organizations, such as AV-Comparatives, SE Labs and MITRE, has consistently ranked CrowdStrike Falcon® as a top performer in automated detection and protection capabilities.
This attack is a good example of how adversaries continue to refine their tradecraft to try and evade security technologies. At CrowdStrike, we’re committed to delivering the technology, intelligence and expertise customers need to stop attackers where they land — and ultimately prevent breaches.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
| File | SHA256 |
| Cryptocurrency miner | 7f986cd3c946f274cdec73f80b84855a77bc2a3c765d68897fbc42835629a5d5 |
| DanaBot loader DLL | 2a3acdcd76575762b18c18c644a745125f55ce121f742d2aad962521bc7f25fd |
Additional Resources
- Read CISA’s public US-CERT Alert issued on Oct. 22, 2021, urging users and administrators to update to patched versions.
- Read these blogs to learn how the Falcon platform protects against StellarParticle’s malware used in the SolarWinds supply chain attack: SUNSPOT: An Implant in the Build Process and Stellar Performances: How CrowdStrike Machine Learning Handles the SUNSPOT Malware.
- Visit the product website to learn how the powerful CrowdStrike Falcon® platform provides comprehensive protection across your organization, workers and data, wherever they are located.
- Get a full-featured free trial of CrowdStrike Falcon® Prevent™ and learn how true next-gen AV performs against today’s most sophisticated threats.