As the year draws to a close, the active exploitation of Microsoft vulnerabilities continues unabated. Once again, a broad range of Microsoft products are included in this month’s Patch Tuesday update as the aging Microsoft ship is springing security leaks everywhere. Two vulnerabilities, CVE-2021-42292 and CVE-2021-42321, have seen in-the-wild exploitation, and four other vulnerabilities were publicly disclosed before Microsoft issued updates, giving threat actors the opportunity to take advantage of them before patches were released.
Given the sheer volume of vulnerabilities in Microsoft products, organizations need to prioritize which vulnerabilities to patch first so they can allocate resources. Severity ratings and scores, while an important indicator of a vulnerability's impact, are not the only measure that SecOps staff should consider in this process. The context and threat intelligence surrounding a particular CVE may indicate a more pressing need to prioritize and mitigate one vulnerability over another. Regular patching cycles and prompt updating are of critical importance for maintaining a strong and defensible security posture.
For assistance on how to determine which vulnerabilities truly affect your organization, see Falcon Spotlight’s ExPRT.AI dynamic model and intelligent rating.
New Patches for 55 Vulnerabilities
November 2021 Patch Tuesday covers fixes for 55 vulnerabilities, with the most common attack types again being remote code execution and elevation of privilege. Microsoft has offered patches for multiple zero-day vulnerabilities surrounding Microsoft Exchange products this year (see March’s Patch Tuesday release), CVE-2021-42321 is a Remote Code Execution vulnerability but requires some authentication and hence won’t see that wide active exploitation. CVE-2021-42292, however, impacts Microsoft Excel products, a widely used application for many organizations — and since this method of attack (security feature bypass) has seen success, this CVE is another one to prioritize in your organization’s patching process.
As with previous months, Windows is a common product to receive patches, and this month includes Extended Security Updates (ESU) and Azure.
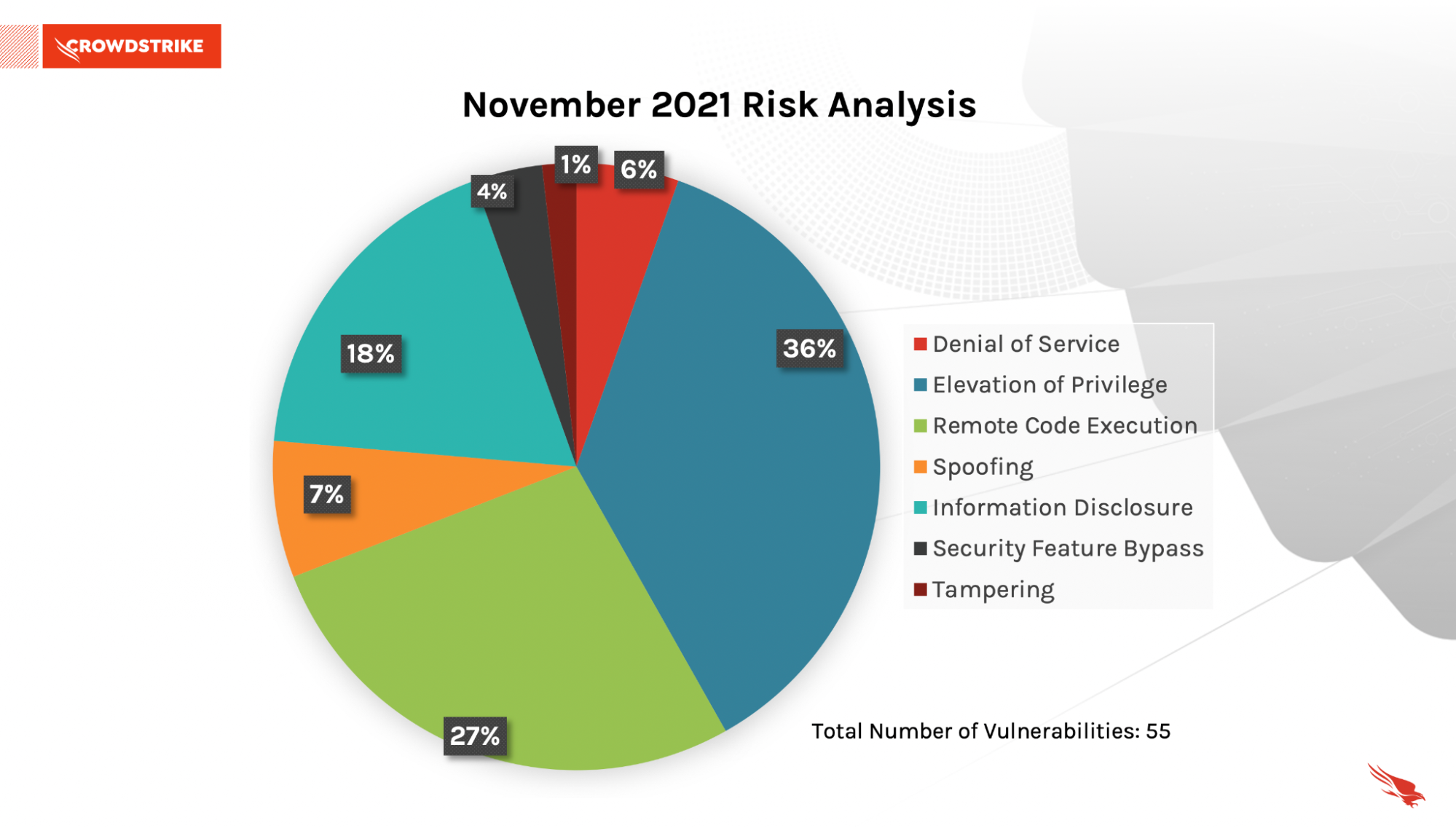 Figure 1. Breakdown of November 2021 Patch Tuesday attack impact
Figure 1. Breakdown of November 2021 Patch Tuesday attack impact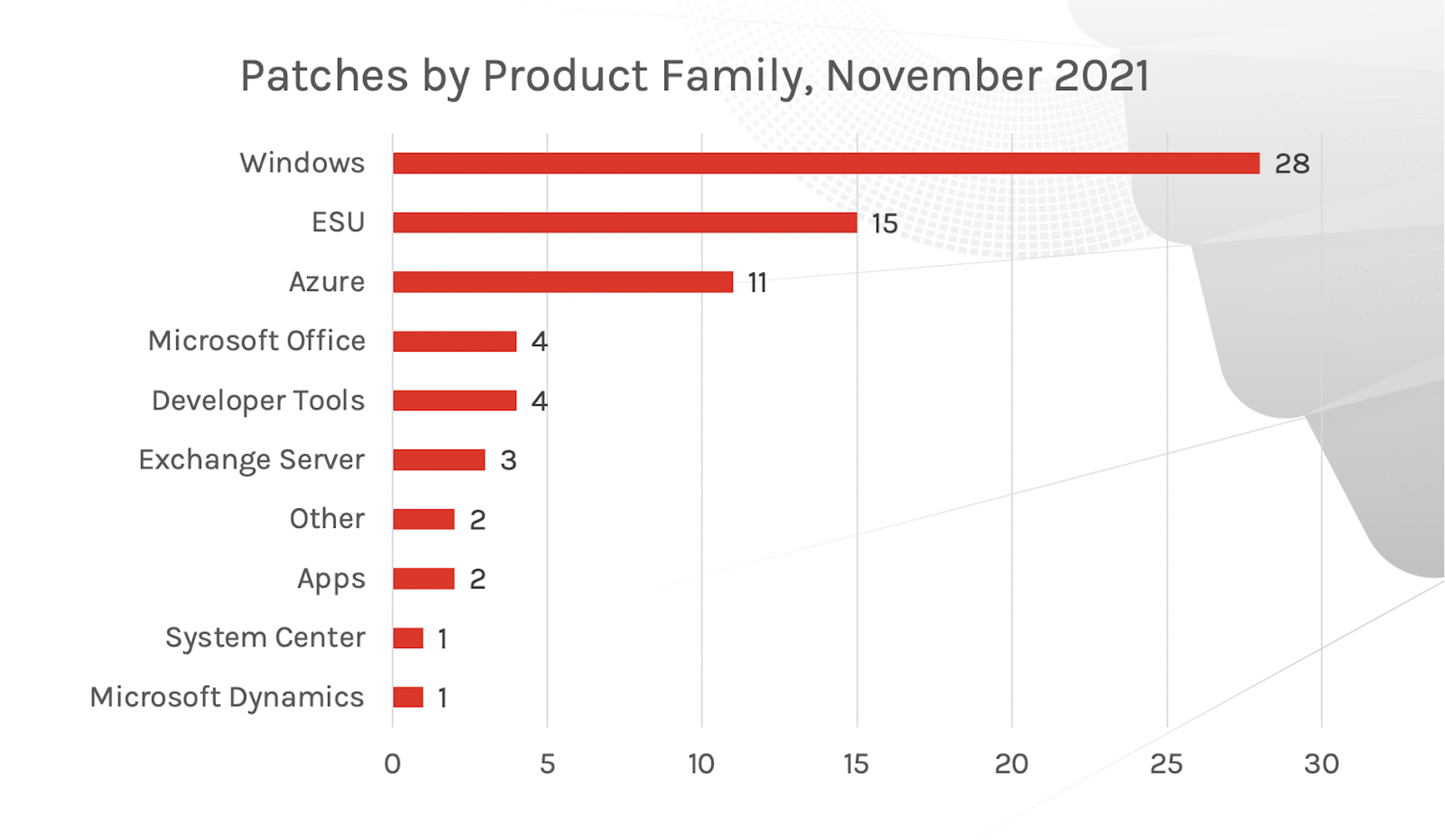 Figure 2. Patches by Product Family
Figure 2. Patches by Product FamilyMore on Active Exploitation for Microsoft Exchange and Microsoft Excel Products
The two zero-day vulnerabilities reported by Microsoft as being exploited in the wild, one affecting Exchange Server and the other impacting Excel, are common access points for attackers to infiltrate an organization.
CVE-2021-42321 is a post-authentication remote code execution vulnerability affecting on-premises Microsoft Exchange Server Exchange 2016 and 2019, including those used by customers in Exchange Hybrid mode. Microsoft has a CVSS of 8.8 for this vulnerability. This vulnerability was successfully exploited during the Tianfu Cup 2021 hacker contest (the Chinese version of Pwn2Own)
CVE-2021-42292 is an actively exploited Microsoft Excel vulnerability utilizing security feature bypass. Adversaries are able to install malicious code by tricking users into opening a “booby-trapped” Excel file. Updates are available for Windows, but as of this writing, an update has not been released for the Mac version.
| Rank | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Critical | 8.8
| CVE-2021-42321 | Microsoft Exchange Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 7.8 | CVE-2021-42292
| Microsoft Excel Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
Publicly Disclosed Vulnerabilities by Microsoft
Four of the vulnerabilities patched by Microsoft this month were publicly disclosed before Microsoft released security updates. Two affect 3D Viewer and can be exploited to gain remote code execution. The other two are related to Windows Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) which can lead to information disclosures. CVE-2021-43208 and CVE-2021-43209 is a 3D Viewer Remote Code Execution vulnerability. These vulnerabilities are publicly disclosed — ZDI published details in June and July 2021. Patches were rolled out from Microsoft Store and customers don’t need to install any KB. CVE-2021-38631 and CVE-2021-41371 is a Windows Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) information disclosure vulnerability. The attacker on successfully exploiting this vulnerability could obtain read access to Windows RDP client passwords set by RDP server administrators.
| Rank | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Important | 4.4 | CVE-2021-38631 | Windows Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| Important | 4.4 | CVE-2021-41371 | Windows Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| Important | 7.8 | CVE-2021-43208 | 3D Viewer Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Important | 7.8 | CVE-2021-43209 | 3D Viewer Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Other Critical Vulnerabilities to Prioritize
CVE-2021-26443, a Microsoft Virtual Machine Bus (VMBus) Remote Code Execution vulnerability, occurs when a VM guest fails to properly handle communication on a VMBus channel. To exploit the vulnerability, an authenticated attacker could send a specially crafted communication on the VMBus channel from the guest VM to the host. An attacker that successfully exploits the vulnerability could execute arbitrary code on the host operating system. CVE-2021-42279, Chakra Scripting Engine Memory Corruption vulnerability, has been given a base score of 4.2 by Microsoft, but it is ranked Critical. It affects almost all versions of Windows 10 and allows an attacker to remotely execute malicious code on the affected system. CVE-2021-42298, a Microsoft Defender Remote Code Execution vulnerability, can lead to malicious remote code execution. Windows Defender uses the Microsoft Malware Protection Engine (mpengine.dll), which provides scanning, detection and cleaning capabilities for Microsoft antivirus and antispyware software. The patch for this vulnerability is automatically downloaded and installed only if the host is set for automatic updating.
| Rank | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Critical
| 9.0 | CVE-2021-26443 | Microsoft Virtual Machine Bus (VMBus) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical
| 9.8 | CVE-2021-3711 | OpenSSL: CVE-2021-3711 SM2 Decryption Buffer Overflow |
| Critical
| 8.8 | CVE-2021-38666 | Remote Desktop Client Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical
| 4.2 | CVE-2021-42279 | Chakra Scripting Engine Memory Corruption Vulnerability |
| Critical
| 7.8 | CVE-2021-42298 | Microsoft Defender Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical
| 8.7 | CVE-2021-42316 | Microsoft Dynamics 365 (on-premises) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 7.8 | CVE-2021-42298 | Microsoft Defender Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
When Priorities Conflict Due to Broad Product Updates Consider Your Prioritization Process
A wide range of vulnerabilities are being patched by Microsoft this month, from operating system patches and known protocols such as RDP to actively exploited vulnerabilities in Microsoft Exchange and Microsoft Excel — and any of these could greatly impact an organization's security posture. SecOps often do not have the time or capacity to patch everything ranked highly within their organization and would do best to tap into the knowledge and solutions that can most accurately assess which vulnerabilities to prioritize first. CrowdStrike has a continued commitment to providing SecOps teams with relevant and timely information around trending threats and valuable insight surrounding vulnerabilities — and with solutions such as Falcon Spotlight, staff can quickly target those vulnerabilities that post the most risk. Falcon Spotlight’s newly released ExPRT Rating examines all relevant data to help organizations predict and prioritize those vulnerabilities relevant to their organization.
Learn More
Watch this video on Falcon Spotlight™ vulnerability management to see how you can quickly monitor and prioritize vulnerabilities within the systems and applications in your organization.
About CVSS Scores
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a free and open industry standard that CrowdStrike and many other cybersecurity organizations use to assess and communicate software vulnerabilities’ severity and characteristics. The CVSS Base Score ranges from 0.0 to 10.0, and the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) adds a severity rating for CVSS scores. Learn more about vulnerability scoring in this article.
Additional Resources
- Learn more on how Falcon Spotlight can help you discover and manage vulnerabilities in your environments.
- See how Falcon Complete stops Microsoft exchange server zero-day exploits.
- Make prioritization painless and efficient. Watch how Falcon Spotlight enables IT staff to improve visibility with custom filters and team dashboards.
- Read last month’s Patch Tuesday for more information on critical vulnerabilities your organization should prioritize.
- Learn about the recent Baron Samedit vulnerability and CrowdStrike’s custom dashboard.
- Test CrowdStrike next-gen AV for yourself. Start your free trial of Falcon Prevent™ today.




![Helping Non-Security Stakeholders Understand ATT&CK in 10 Minutes or Less [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/video-ATTCK2-1)
![Qatar’s Commercial Bank Chooses CrowdStrike Falcon®: A Partnership Based on Trust [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/Edward-Gonam-Qatar-Blog2-1)













































