Microsoft has released 75 security patches for its February 2023 Patch Tuesday rollout: 9 vulnerabilities are rated Critical, and the remaining 66 are rated Important.
Three actively exploited vulnerabilities were reported by the vendor: an elevation of privilege within Windows Common Log File System Driver (CVE-2023-23376), a security feature bypass in Microsoft Office (CVE-2023-21715), and a remote code execution security flaw in Windows Graphics Component (CVE-2023-21823).
February 2023 Risk Analysis
This month’s leading risk type is Remote Code Execution (48%, up from 34% in January 2023), followed by Elevation of Privilege at nearly 16% (down from nearly 40% in January), and Denial of Service at 13% (up from 10% last month).
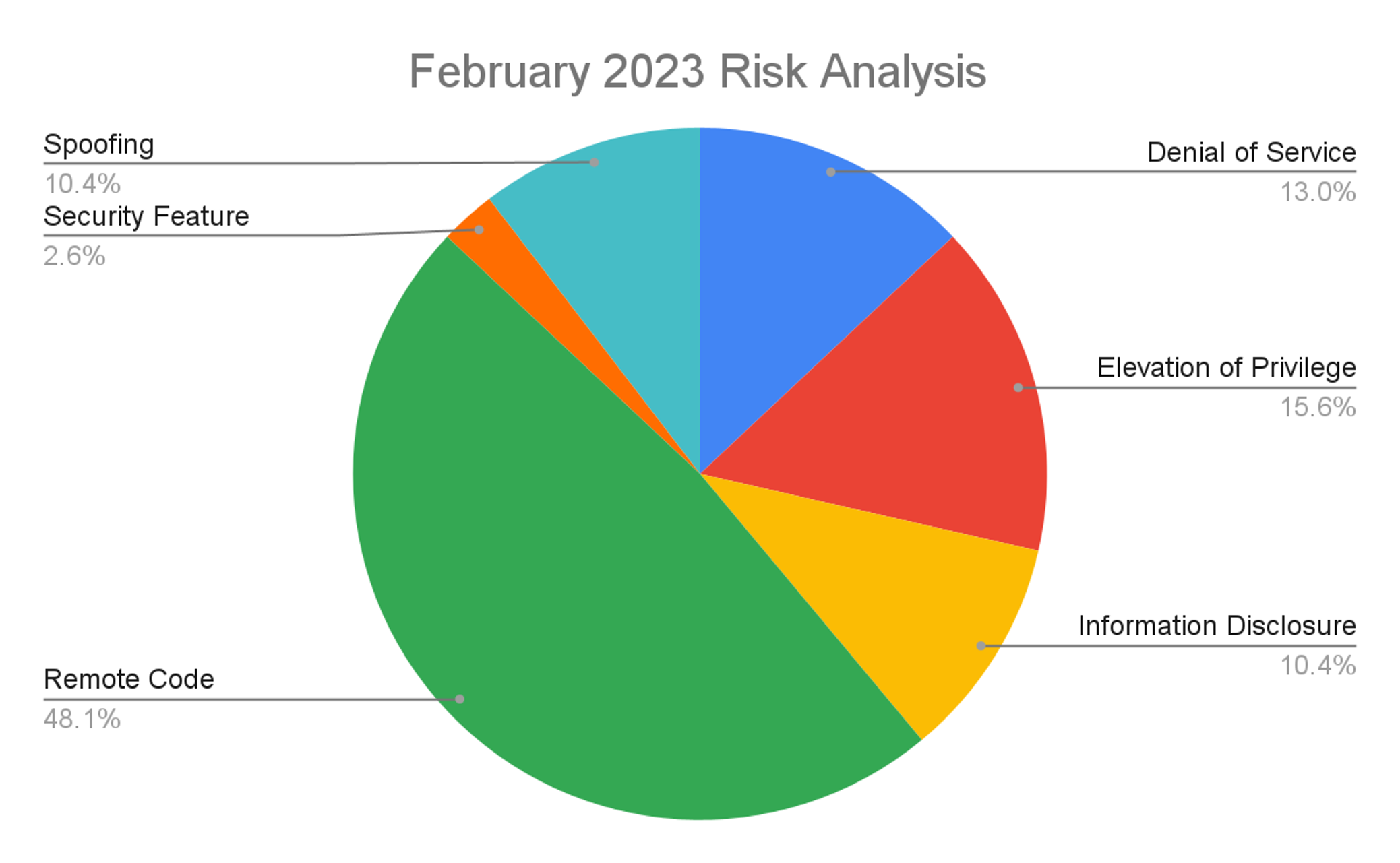 Figure 1. Breakdown of February 2023 Patch Tuesday attack types
Figure 1. Breakdown of February 2023 Patch Tuesday attack typesThe Microsoft Windows product family received the most patches this month (36), followed by Extended Support Updates (34), and SQL Server and Developer Tools (such as Visual Studio Code) with seven patches each.
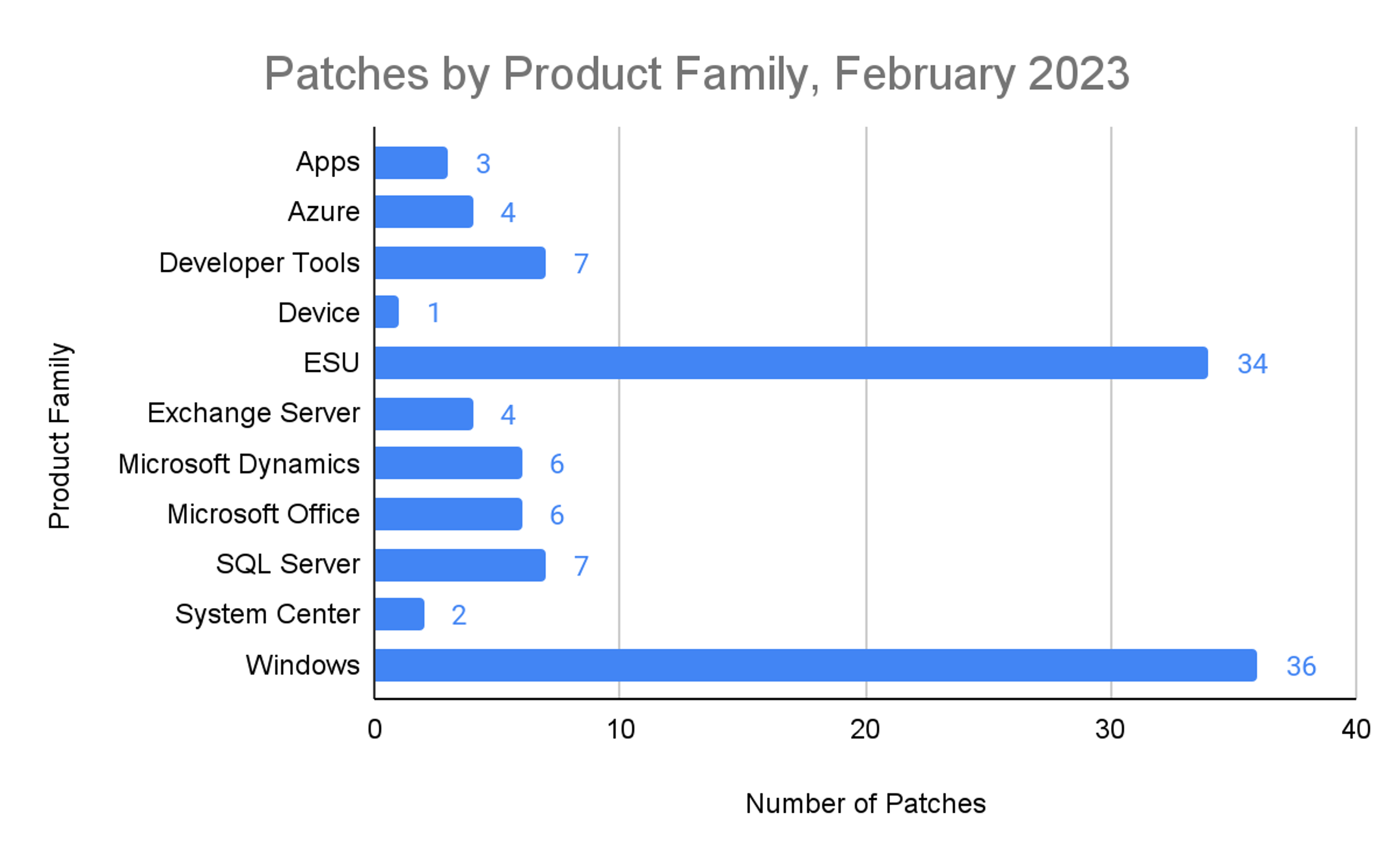 Figure 2. Breakdown of product families affected by February 2023 Patch Tuesday
Figure 2. Breakdown of product families affected by February 2023 Patch TuesdayActively Exploited Vulnerabilities
CVE-2023-21823, rated Important, is a vulnerability affecting Windows Graphics Component. This zero-day was discovered by Genwei Jiang and Dhanesh Kizhakkinan of Mandiant. No additional data was provided by Microsoft at this time. It is recommended to patch the operating system in order to mitigate this vulnerability.
CVE-2023-23376, rated Important, is an elevation of privilege security flaw that impacts the Common Log File System(CLFS) Driver, a logging service used by both kernel- and user-mode applications. This vulnerability can be leveraged after an attacker has obtained access to a vulnerable target in order to elevate to SYSTEM privileges. The flaw was discovered by the Microsoft Threat Intelligence Center (MSTIC) and Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC).
CVE-2023-21715, also rated Important, is a security flaw allowing an attacker to bypass Microsoft Office macro policies that are used to block untrusted or malicious files. An authenticated attacker could exploit the vulnerability by convincing a victim, through social engineering, to download from a website and open a specially crafted file that could lead to a local attack on the victim computer.
| Rank | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Important | 7.8 | CVE-2023-21823 | Windows Graphics Component Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Important | 7.8 | CVE-2023-23376 | Windows Common Log File System Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Important | 7.3 | CVE-2023-21715 | Microsoft Publisher Security Features Bypass Vulnerability |
Figure 3. Actively exploited vulnerabilities patched in February 2023
Critical Vulnerabilities in Microsoft Products
Critical Vulnerabilities in Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP)
CVE-2023-21692, CVE-2023-21690 and CVE-2023-21689 are extremely dangerous vulnerabilities, all with a CVSS 9.8 score. To exploit these vulnerabilities, an attacker sends specially crafted PEAP packets over the network to a victim machine, potentially allowing for remote code execution in the user context of the targeted network account. An attacker does not require special privileges or user interaction in order to exploit this vulnerability. However, Microsoft notes that PEAP is only negotiated if the Network Policy Server Service (NPS) is running on the Windows Server endpoint and has a network policy configured to allow PEAP. To stop using PEAP, Microsoft recommends customers ensure that PEAP type is not configured as an allowed EAP type in their network policy. To learn more, Microsoft recommends visiting Configure the New Wireless Network Policy and Configure Network Policies.
| Rank | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Critical | 9.8 | CVE-2023-21692 | Microsoft Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 9.8 | CVE-2023-21690 | Microsoft Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 9.8 | CVE-2023-21689 | Microsoft Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Figure 4. Critical vulnerabilities in PEAP
Critical Vulnerabilities Affecting Microsoft Word
Deemed “less likely exploitable” by Microsoft, CVE-2023-21716 is a remote code execution vulnerability affecting Microsoft Word, Sharepoint, Office 365 and Office for Mac and has been assigned a CVSS score of 9.8. The vulnerability does not require authentication and could be exploited by sending an email with a rich text format (RTF) payload that, when opened, leads to a command execution.
For more guidance on how to prevent Word from loading RTF files, refer to MS08-026.
| Rank | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Critical | 9.8 | CVE-2023-21716 | Microsoft Word Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Figure 5. Critical vulnerabilities in MS Word
Critical Vulnerabilities Affecting Visual Studio Code
CVE-2023-23381 and CVE-2023-21815 are arbitrary code execution vulnerabilities targeting the Visual Studio Code. This means that while the impact is remote code execution, the adversary must be able to run code on the victim machine to exploit the vulnerability. In other words, the adversary sends a crafted file to the victim computer and then the victim runs the malicious code. Microsoft recommends updating to the most recent version of Visual Studio Code in order to mitigate this vulnerability.
| Rank | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Critical | 8.4 | CVE-2023-23381 | Visual Studio Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 8.4 | CVE-2023-21815 | Visual Studio Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Figure 6. Critical vulnerabilities affecting Visual Studio Code
Critical Vulnerabilities Affecting Windows iSCSI Discovery Service
CVE-2023-21803 could allow an attacker the ability to remotely execute code on a target system. By default, the iSCSI Initiator client application is disabled, and in this state, an attacker cannot exploit this vulnerability. For a system to be vulnerable, the iSCSI Initiator client application would need to be enabled. Only x86 or 32-bit based versions of Windows are affected by this vulnerability.
| Rank | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Critical | 9.8 | CVE-2023-21803 | Windows iSCSI Discovery Service Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Figure 7. Critical vulnerabilities affecting Windows iSCSI Service
Not All Relevant Vulnerabilities Have Patches: Consider Mitigation Strategies
As we have learned with other notable vulnerabilities, such as Log4j, not every highly exploitable vulnerability can be easily patched. As is the case for the ProxyNotShell vulnerabilities, it’s critically important to develop a response plan for how to defend your environments when no patching protocol exists.
Regular review of your patching strategy should still be a part of your program, but you should also look more holistically at your organization's methods for cybersecurity and improve your overall security posture.
The CrowdStrike Falcon platform collects and analyzes trillions of endpoint events every day from millions of sensors deployed across 176 countries. Watch this demo to see the Falcon platform in action.
Learn More
This video on CrowdStrike Falcon® Spotlight vulnerability management shows how you can quickly monitor and prioritize vulnerabilities within the systems and applications in your organization.
About CVSS Scores
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a free and open industry standard that CrowdStrike and many other cybersecurity organizations use to assess and communicate software vulnerabilities’ severity and characteristics. The CVSS Base Score ranges from 0.0 to 10.0, and the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) adds a severity rating for CVSS scores. Learn more about vulnerability scoring in this article.
Additional Resources
- Download the CrowdStrike 2022 Falcon OverWatch Threat Hunting Report to learn more about recent adversary tradecraft and tooling and get actionable tips for staying ahead of today's stealthiest, most sophisticated cyber threats.
- See how Falcon Spotlight can help you discover and manage vulnerabilities in your environments.
- Learn how the new External Attack Surface Module, Falcon Surface (EASM) can discover unknown, exposed and vulnerable internet-facing assets enabling security teams to stop adversaries in their tracks.
- Learn how Falcon Identity Protection products can stop workforce identity threats faster.
- Make prioritization painless and efficient. Watch how Falcon Spotlight enables IT staff to improve visibility with custom filters and team dashboards.
- Test CrowdStrike next-gen AV for yourself with a free trial of Falcon Prevent.



![Helping Non-Security Stakeholders Understand ATT&CK in 10 Minutes or Less [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/video-ATTCK2-1)
![Qatar’s Commercial Bank Chooses CrowdStrike Falcon®: A Partnership Based on Trust [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/Edward-Gonam-Qatar-Blog2-1)