Microsoft has released patches for 38 vulnerabilities for its May 2023 Patch Tuesday rollout: 6 are rated as Critical while the remaining 32 are rated as Important. Three vulnerabilities are identified as actively exploited (zero days).
May 2023 Risk Analysis
This month’s leading risk type is remote code execution (RCE) — 32%, down from 46.4% in April 2023 — followed by elevation of privilege (21%, up from 20.6% in April) and information disclosure (21%, up from 10.3% in April).
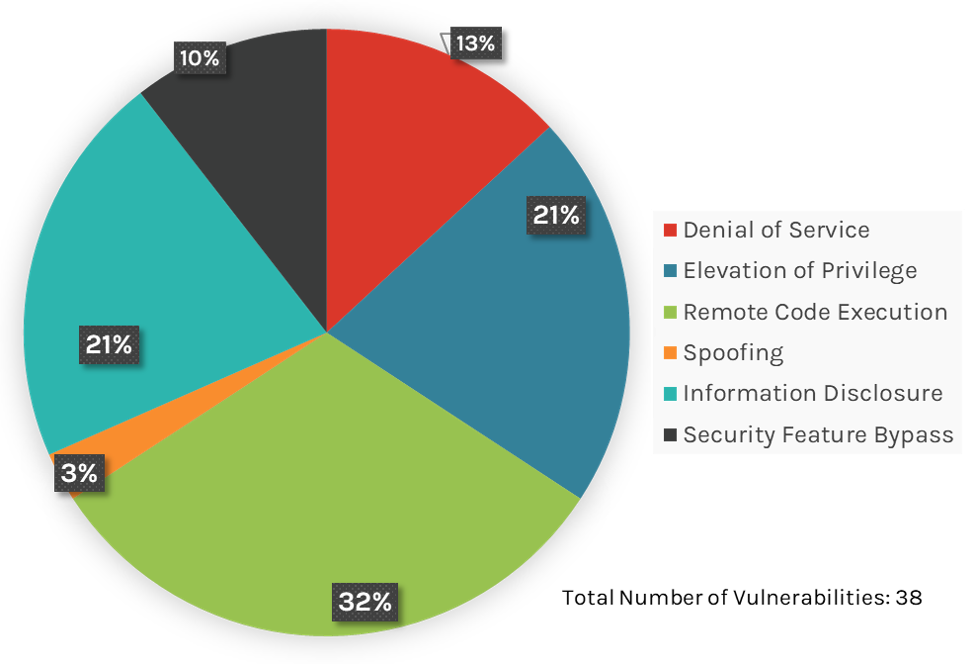 Figure 1. Breakdown of May 2023 Patch Tuesday attack types
Figure 1. Breakdown of May 2023 Patch Tuesday attack types
The Microsoft Windows product family received the most patches this month with 27, followed by Extended Support Updates (14) and Microsoft Office products (8).
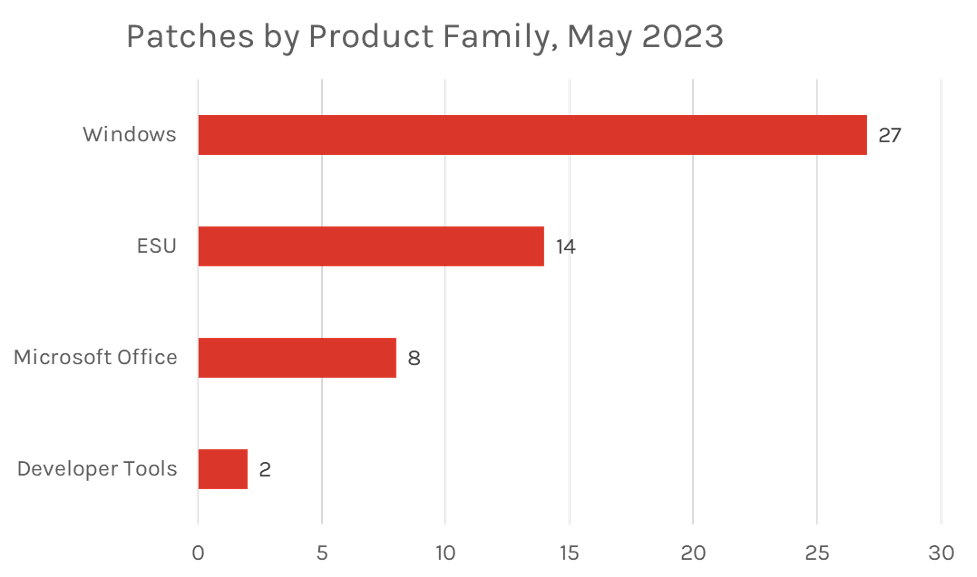 Figure 2. Breakdown of product families affected by May 2023 Patch Tuesday
Figure 2. Breakdown of product families affected by May 2023 Patch Tuesday
Actively Exploited Zero-Day Vulnerability Affects Windows OLE
CVE-2023-29325 is a Critical race condition vulnerability affecting Windows OLE (Object Linking and Embedding). Per Microsoft, “In an email attack scenario, an attacker could exploit the vulnerability by sending the specially crafted email to the victim. Exploitation of the vulnerability might involve either a victim opening a specially crafted email with an affected version of Microsoft Outlook software, or a victim's Outlook application displaying a preview of a specially crafted email. This could result in the attacker executing remote code on the victim's machine.”
Actively Exploited Zero-Day Vulnerability Affects Windows Win32k
CVE-2023-29336 is rated as Important by Microsoft. An attacker that successfully exploited this vulnerability could gain SYSTEM privileges. Microsoft has not reported how this is being abused. However, given that this vulnerability was reported by antivirus company Avast, one can be fairly certain this is already being exploited in the wild.
Actively Exploited Zero-Day Vulnerability Affects Windows Secure Boot Feature
CVE-2023-24932, rated as Important, affects the Windows Secure Boot security feature. Secure Boot is designed to prevent malicious software from loading when a PC starts up. This is being exploited in the wild by the BlackLotus bootkit, which chains this vulnerability to exploit CVE-2022-21894. Microsoft reports this also affects some virtual machines or cloud-based devices, as well as Linux distributions, and it is working with representatives from major Linux distributions to mitigate this issue.
Per Microsoft, “To exploit the vulnerability, an attacker who has physical access or Administrative rights to a target device could install an affected boot policy.” According to Microsoft, there are additional steps along with the update to mitigate: “The security update addresses the vulnerability by updating the Windows Boot Manager, but is not enabled by default. Additional steps are required at this time to mitigate the vulnerability. Please refer to the following for steps to determine impact on your environment: KB5025885: How to manage the Windows Boot Manager revocations for Secure Boot changes associated with CVE-2023-24932.”
| Severity | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Critical | 8.1 | CVE-2023-29325 | Windows OLE Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Important | 7.8 | CVE-2023-29336 | Win32k Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Important | 6.7 | CVE-2023-24932 | Windows Secure Boot Security Feature Bypass |
Figure 3. Zero-day vulnerabilities patched in May 2023
CVE-2023-24941 is a Critical vulnerability affecting Windows Network File System. Microsoft says, “This vulnerability could be exploited over the network by making an unauthenticated, specially crafted call to a Network File System (NFS) service to trigger a Remote Code Execution (RCE).” Microsoft reports this vulnerability is not exploitable in NFSV2.0 or NFSV3.0. For those affected, Microsoft provides mitigation instructions that should be followed ONLY if the May 2022 Windows security updates have been installed.
CVE-2023-24943 is a Critical vulnerability affecting Windows Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM). “When Windows Message Queuing service is running in a PGM Server environment, an attacker could send a specially crafted file over the network to achieve remote code execution and attempt to trigger malicious code,” Microsoft says.
CVE-2023-24903 is a Critical vulnerability affecting Windows Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP). According to Microsoft, “Successful exploitation of this vulnerability requires an attacker to win a race condition. To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker would need to send a specially crafted malicious SSTP packet to a SSTP server. This could result in remote code execution on the server side.”
CVE-2023-28283 is a Critical vulnerability affecting Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). Another race condition vulnerability could allow an unauthenticated attacker that successfully exploited this vulnerability to gain code execution through a specially crafted set of LDAP calls to execute arbitrary code within the context of the LDAP service.
CVE-2023-24955 is a Critical vulnerability affecting Microsoft SharePoint Servers that could allow an authenticated user, as a Site Owner, to execute code remotely on the SharePoint Server.
CVE-2023-29324 is a Critical vulnerability affecting the Windows MSHTML Platform security feature. An attacker can craft a malicious URL that would evade zone checks, resulting in a limited loss of integrity and availability of the victim machine. While Microsoft has announced retirement of the Internet Explorer 11 application on certain platforms and the Microsoft Edge Legacy application is deprecated, the underlying MSHTML, EdgeHTML and scripting platforms are still supported. This means other applications could still rely on the vulnerable underlying DLLs.
| Severity | CVSS Score | CVE | Description |
| Critical | 9.8 | CVE-2023-24941 | Windows Network File System Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 9.8 | CVE-2023-24943 | Windows Pragmatic General Multicast (PGM) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 8.1 | CVE-2023-24903 | Windows Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 8.1 | CVE-2023-28283 | Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 7.2 | CVE-2023-24955 | Microsoft SharePoint Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| Critical | 6.5 | CVE-2023-29324 | Windows MSHTML Platform Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
Figure 4. Critical vulnerabilities patched in May 2023
Not All Relevant Vulnerabilities Have Patches: Consider Mitigation Strategies
As we have learned with other notable vulnerabilities, such as Log4j, not every highly exploitable vulnerability can be easily patched. As is the case for the ProxyNotShell vulnerabilities, it’s critically important to develop a response plan for how to defend your environments when no patching protocol exists. Regular review of your patching strategy should still be a part of your program, but you should also look more holistically at your organization's methods for cybersecurity and improve your overall security posture. The CrowdStrike Falcon® platform regularly collects and analyzes trillions of endpoint events a day from millions of sensors deployed across 176 countries. Watch this demo to see the Falcon platform in action.
Learn More
Learn more about how CrowdStrike Falcon® Spotlight can help you quickly and easily discover and prioritize vulnerabilities here.
About CVSS Scores
The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is a free and open industry standard that CrowdStrike and many other cybersecurity organizations use to assess and communicate software vulnerabilities’ severity and characteristics. The CVSS Base Score ranges from 0.0 to 10.0, and the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) adds a severity rating for CVSS scores. Learn more about vulnerability scoring in this article.
Additional Resources
- For more information on which products are in Microsoft’s Extended Security Updates program, refer to the vendor guidance here.
- Download the CrowdStrike 2023 Global Threat Report to learn how the threat landscape has shifted in the past year and understand the adversary behavior driving these shifts.
- See how CrowdStrike Falcon® Spotlight can help you discover and manage vulnerabilities and prioritize patches in your environments.
- Learn how CrowdStrike’s external attack surface module, CrowdStrike Falcon® Surface, can discover unknown, exposed and vulnerable internet-facing assets enabling security teams to stop adversaries in their tracks.
- Learn how Falcon identity protection products can stop workforce identity threats faster.
- Make prioritization painless and efficient. Watch how Falcon Spotlight enables IT staff to improve visibility with custom filters and team dashboards.
- Test CrowdStrike next-gen AV for yourself with a free trial of CrowdStrike Falcon® Prevent.




![Helping Non-Security Stakeholders Understand ATT&CK in 10 Minutes or Less [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/video-ATTCK2-1)
![Qatar’s Commercial Bank Chooses CrowdStrike Falcon®: A Partnership Based on Trust [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/Edward-Gonam-Qatar-Blog2-1)
![Endpoint Protection and Threat Intelligence: The Way Forward [VIDEO]](https://assets.crowdstrike.com/is/image/crowdstrikeinc/GK-Blog_Images-1)