“Sin”-ful SPIDERS: WIZARD SPIDER and LUNAR SPIDER Sharing the Same Web
CrowdStrike® Intelligence observed a new campaign from a LUNAR SPIDER affiliate to distribute WIZARD SPIDER’s TrickBot malware on Feb. 7, 2019. However, this latest campaign is somewhat unique due to a custom variant of a TrickBot module that (to date) is only associated with this campaign.
The WIZARD SPIDER threat group is the Russia-based operator of the TrickBot banking malware. This group represents a growing criminal enterprise of which GRIM SPIDER appears to be a subset. The LUNAR SPIDER threat group is the Eastern European-based operator and developer of the commodity banking malware called BokBot (aka IcedID), which was first observed in April 2017. The BokBot malware provides LUNAR SPIDER affiliates with a variety of capabilities to enable credential theft and wire fraud, through the use of webinjects and a malware distribution function.
Campaigns involving both BokBot and TrickBot were first identified by CrowdStrike Intelligence in July 2017. In these campaigns, victim machines infected with BokBot issued a command to download and execute a TrickBot payload. A somewhat sporadic relationship between the two adversaries has continued since then, although this most recent campaign likely signals a more intimate phase of that relationship.
TrickBot Distribution
On Feb. 7, 2019, LUNAR SPIDER’s BokBot project ID C610DF9A was seen downloading and executing a loader from http://tfulf[.]host/Sw9HJmXzq.exe. The custom loader subsequently downloaded a TrickBot loader from http://185.68.93[.]30/sin.png. The configuration file of this sample indicates it is TrickBot version 1000351 and belongs to the group tag (gtag) sin2. The gtags with a prefix of sin have been related to LUNAR SPIDER activity as the successor to the previously associated mom gtag prefix.
The full TrickBot configuration file, including command-and-control (C2) servers, can be seen below.
<mcconf> <ver>1000351</ver> <gtag>sin2</gtag> <servs> <srv>185.246.64[.]237:443</srv> <srv>68.119.85[.]138:449</srv> <srv>65.184.200[.]184:449</srv> <srv>185.62.188[.]30:443</srv> <srv>96.36.253[.]146:449</srv> <srv>92.38.135[.]33:443</srv> <srv>24.247.181[.]155:449</srv> <srv>31.131.22[.]212:443</srv> <srv>208.79.106[.]155:449</srv> <srv>192.227.204[.]224:443</srv> <srv>124.29.213[.]74:449</srv> <srv>46.100.14[.]215:449</srv> <srv>190.109.178[.]222:449</srv> <srv>103.47.168[.]172:449</srv> <srv>208.79.110[.]201:449</srv> <srv>204.14.154[.]126:449</srv> <srv>103.47.168[.]72:449</srv> <srv>103.47.168[.]91:449</srv> <srv>46.21.249[.]220:443</srv> <srv>107.146.147[.]235:449</srv> <srv>185.62.188[.]30:443</srv> <srv>68.111.123[.]100:449</srv> <srv>103.47.169[.]27:449</srv> <srv>24.247.182[.]240:449</srv> <srv>36.91.74[.]138:449</srv> <srv>125.209.82[.]158:449</srv> <srv>76.107.90[.]235:449</srv> <srv>47.224.98[.]123:449</srv> <srv>185.222.202[.]79:443</srv> <srv>24.247.182[.]253:449</srv> <srv>216.17.92[.]138:449</srv> <srv>199.21.106[.]189:449</srv> <srv>208.79.106[.]213:449</srv> <srv>24.247.182[.]253:449</srv> <srv>136.25.2[.]43:449</srv> <srv>181.129.93[.]226:449</srv> <srv>170.79.176[.]242:449</srv> </servs> <autorun> <module name="systeminfo" ctl="GetSystemInfo"/> <module name="injectDll"/> <module name="pwgrab"/> </autorun></mcconf>Modified TrickBot Module
This activity follows the previous pattern of BokBot assisting in the delivery of TrickBot. However, the most interesting thing about the custom loader is the embedded, Base64-encoded Portable Executable (PE) file shown in Figure 1.
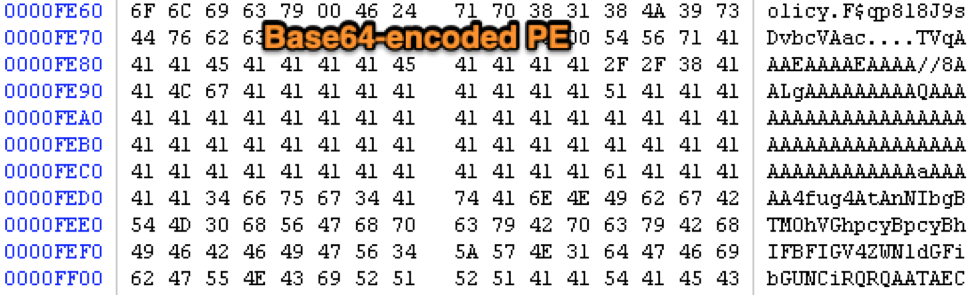
Figure 1. Base64-Encoded PE File
The embedded PE file is extracted by the custom loader, then decoded and executed. Analysis revealed that this decoded PE file is, in fact, a modified version of the TrickBot lateral movement module shareDll. Typically, TrickBot modules are downloaded as a dynamic link library (DLL) with a standard set of exports, named Start, Control and Release. This DLL would then be injected into a child svchost.exe process within the TrickBot modular framework. However, in the absence of this framework, the shareDll module distributed by BokBot is a PE file.
In addition, the strings within a standard TrickBot module are not obfuscated or protected in any way. However, the module distributed by BokBot contains strings that are both encrypted with 256-bit AES, with a derived key and initialization vector (IV), and Base64-encoded with the custom alphabet of terKSDozBw1l24IyCL6AHh/+5WRiGnj3xJQ8YkEbcgOZVNPamMsuUTpd0q9vFfX7. The strings are stored in an encrypted string table (shown in Figure 2) in the exact same way as the main TrickBot loader, and decrypted when they are needed.
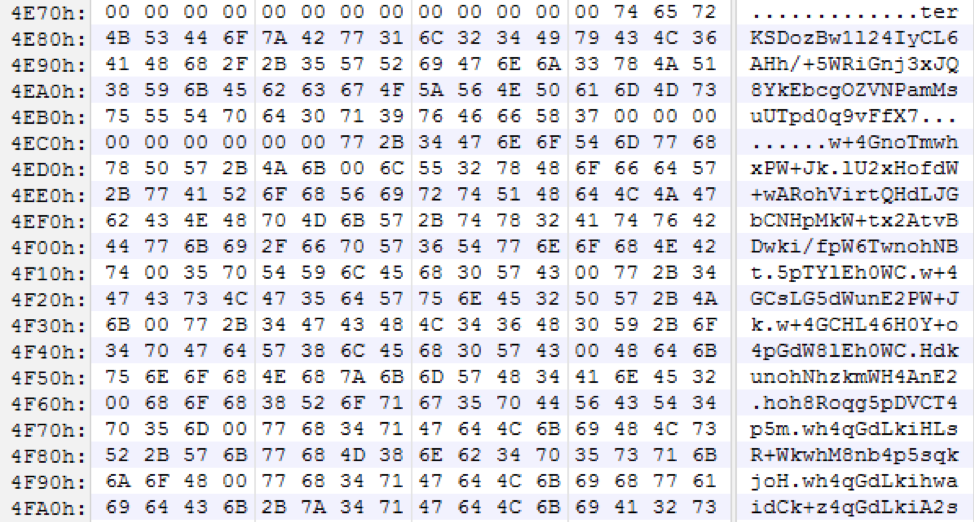
Figure 2. Custom Base64 Alphabet and Encrypted Strings
Table 1 below outlines the key identified differences between the two variants of the shareDll module.
| BokBot Distributed shareDll | TrickBot Distributed shareDll |
| PE file | DLL file |
| Obfuscated | Little or no obfuscation |
| No exports | Start, Control, and Release exports |
Table 1. Compares Key Differences Between Two Variants of ShareDLL
The primary function of the shareDll module in both cases is to attempt lateral movement within the victim’s network, to reach machines accessible by the currently logged-on user. In the BokBot distributed instance, once an accessible machine has been located, the modified spreader module will attempt to download the TrickBot loader located at http://185.68.93[.]30/sin.png or http://185.68.93[.]30/win.png and install TrickBot on the accessible network machine.
The whole process of BokBot installing TrickBot on the local machine and moving laterally around the network is illustrated in Figure 3.
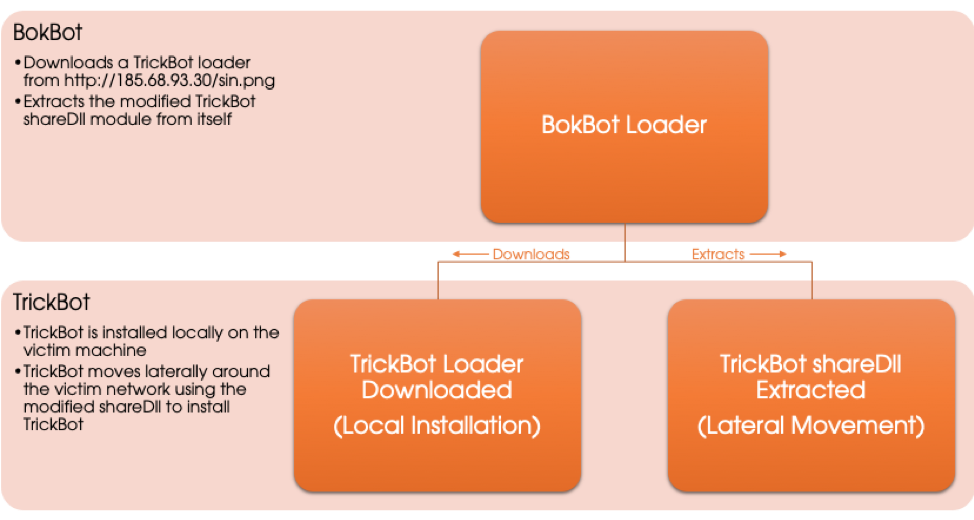
Figure 3. BokBot Installation of TrickBot and Lateral Movement Using ShareDll
Renamed Modules
Beginning on Feb. 8, 2019, CrowdStrike Intelligence observed further development in this intriguing relationship when renamed TrickBot modules were delivered to victims of the gtags sin2 and sin4. These gtags have been closely associated with LUNAR SPIDER activity. The renamed modules and their respective SHA256 hashes are shown in Table 2 and contain the strings sin, tin, and win.
| Module Name | Module SHA256 Hash |
sharesinDll32 |
eefd209ba6afff5830d5510e68b2af90df200550d8ca4c40029baa93a0f01999 |
sharesinDll32 |
1b84f604847be0dbdf19ca169deb22b0245ca6f4bc2877b7a0ceeffa0436d7b3 |
sharesinDll32 |
ea3c70d82f3b4fe8d0914cc58669da0f3f116aa20f0661d68f826fd55763ef50 |
sharesinDll64 |
93da209d2fdb49df19b53089bb1820aa0183e9f207ea87b51b49faa74f8e76ba |
sharesinDll64 |
915e416576be4b459c19941cc86a84fb0d66f54964552be0f69045b89323d2f7 |
sharesinDll64 |
6d8551194b12655b4605f046a754257f69b1ee250f21e32466db54797a45c7c0 |
tabtinDll32 |
aa074b7a1ce29abd9141dc18ca603f2ed2764ae1afabb92eb2f9e4dc008d99d6 |
tabtinDll32 |
ba5bd732466a41636217b639a7a2aff1038a80bc29bd80c0532609d53297051f |
tabtinDll64 |
7023bbd875635b35fdc0eba303143be76afb50c0f34e8d79e8d0daba1d984b60 |
tabtinDll64 |
13b8ab8ce0aa9db161c065c6bf2fdbb50c6fd82fe48e4576abc4b8c3136f925e |
wormwinDll32 |
cac2f117d8b4f1fc40dd0921ea91312ad8129df3556444e41fda8d27c81e02cd |
wormwinDll32 |
d51644cefd34dd7e1ec32a3e0336f9c479c196527e8baea6e85937254cecfe99 |
wormwinDll64 |
8c20b33374c280e9fd98113304843a339f738647cc13daf8f60312b9fef6b702 |
wormwinDll64 |
e8ecceb0cbc0e6aefab5ac47a9e69f7926317d9e4f9a782b8df418c67a8d0661 |
Table 2. Renamed Modules and Associated SHA256 Hashes
Unlike the changes identified in the TrickBot module shareDll being distributed by BokBot, the modules sharesinDll, tabtinDll, and wormwinDll remain functionally equivalent to the TrickBot deployed modules shareDll, tabDll, and wormDll, respectively, and retain the typical characteristics of a TrickBot module. More explicitly, the modules are DLLs, contain no encrypted strings, and have the standard TrickBot exports of Start, Control, and Release.
CrowdStrike Falcon®®endpoint provides protection coverage against these threats through behavioral IOA and machine learning.
Conclusion
It is unclear at this stage what purpose the module renaming serves, but it may be a method of tracking activity from those modules specifically associated with the aforementioned gtags. Additionally, CrowdStrike Intelligence is exploring a possible connection between the TrickBot affiliate operating sin-prefixed TrickBot gtags and the BokBot affiliate operating the project ID C610DF9A, due to the recent introduction of the previously mentioned custom TrickBot module. Of note, BokBot has aided the distribution of TrickBot, with the standard module set, through other BokBot project IDs for some time.
Another key point to note about this recent development is the historical relationship that previously existed between the developers and operators of the banking malware families Dyre (aka Dyreza) and Neverquest (aka Vawtrak). This relationship is key because:
- WIZARD SPIDER includes members that were a part of the same group that had developed and operated Dyre.
- LUNAR SPIDER includes members that were a part of the same group that had developed and operated Neverquest.
Despite being successful malware operations, both Dyre and Neverquest suddenly ceased operating in November 2015 and May 2017, respectively (Figure 4). LUNAR SPIDER had already introduced BokBot to the criminal market at the time Neverquest operations ceased, suggesting that the malware change may have been planned.
Conversely, the Dyre operation ceased following Russian law enforcement action in which the offices of a Moscow-based film and production company, named 25th Floor, were raided in November 2015. Although no details were released by Russian law enforcement, it was speculated that the office played a part in the operation of Dyre. There was a one-year delay before the release of the TrickBot malware, which contains key similarities to the Dyre malware, but the operation was immediately successful and grew swiftly.
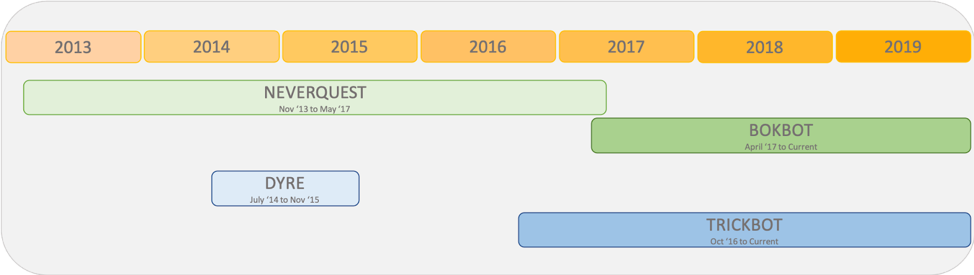
Figure 4. Timeline of Malware Operating Dates
Although BokBot has aided the distribution of TrickBot since 2017, the development of custom TrickBot modules for the specific campaign has not been observed before. This significant development demonstrates a close relationship between the members of LUNAR SPIDER and WIZARD SPIDER. CrowdStrike Intelligence assesses that the historical relationship established during the operations of Dyre and Neverquest has been reinvigorated and solidified now that both WIZARD SPIDER and LUNAR SPIDER have established successful malware operations.
Appendix/Indicators
| Indicator | Description |
http://tfulf[.]host/Sw9HJmXzq.exe |
Custom loader URL |
4ba234160cfbd1ef8ca2a259e51abdd4f6109ce74954fb7541d6226ec510b755 |
Custom loader SHA256 |
http://185.68.93[.]30/sin.png |
TrickBot loader URL |
http://185.68.93[.]30/win.png |
TrickBot loader URL |
d06432486e7e9c2b8aaef4f42c11cf8efe19689638a3512ce931a23bdb5f2b4c |
TrickBot loader SHA256 |
185.246.64[.]237:44368.119.85[.]138:44965.184.200[.]184:449185.62.188[.]30:44396.36.253[.]146:44992.38.135[.]33:44324.247.181[.]155:44931.131.22[.]212:443208.79.106[.]155:449192.227.204[.]224:443124.29.213[.]74:44946.100.14[.]215:449190.109.178[.]222:449103.47.168[.]172:449208.79.110[.]201:449204.14.154[.]126:449103.47.168[.]72:449103.47.168[.]91:44946.21.249[.]220:443107.146.147[.]235:449185.62.188[.]30:44368.111.123[.]100:449103.47.169[.]27:44924.247.182[.]240:44936.91.74[.]138:449125.209.82[.]158:44976.107.90[.]235:44947.224.98[.]123:449185.222.202[.]79:44324.247.182[.]253:449216.17.92[.]138:449199.21.106[.]189:449208.79.106[.]213:44924.247.182[.]253:449136.25.2[.]43:449181.129.93[.]226:449170.79.176[.]242:449 |
TrickBot C2 Servers |
f8967874aeeddfa65f492489dfb91de138e34313bf804d3200423c790eb19dce |
Customized shareDll module |
eefd209ba6afff5830d5510e68b2af90df200550d8ca4c40029baa93a0f01999 |
sharesinDll32 |
1b84f604847be0dbdf19ca169deb22b0245ca6f4bc2877b7a0ceeffa0436d7b3 |
sharesinDll32 |
ea3c70d82f3b4fe8d0914cc58669da0f3f116aa20f0661d68f826fd55763ef50 |
sharesinDll32 |
93da209d2fdb49df19b53089bb1820aa0183e9f207ea87b51b49faa74f8e76ba |
sharesinDll64 |
915e416576be4b459c19941cc86a84fb0d66f54964552be0f69045b89323d2f7 |
sharesinDll64 |
6d8551194b12655b4605f046a754257f69b1ee250f21e32466db54797a45c7c0 |
sharesinDll64 |
aa074b7a1ce29abd9141dc18ca603f2ed2764ae1afabb92eb2f9e4dc008d99d6 |
tabtinDll32 |
ba5bd732466a41636217b639a7a2aff1038a80bc29bd80c0532609d53297051f |
tabtinDll32 |
7023bbd875635b35fdc0eba303143be76afb50c0f34e8d79e8d0daba1d984b60 |
tabtinDll64 |
13b8ab8ce0aa9db161c065c6bf2fdbb50c6fd82fe48e4576abc4b8c3136f925e |
tabtinDll64 |
cac2f117d8b4f1fc40dd0921ea91312ad8129df3556444e41fda8d27c81e02cd |
wormwinDll32 |
d51644cefd34dd7e1ec32a3e0336f9c479c196527e8baea6e85937254cecfe99 |
wormwinDll32 |
8c20b33374c280e9fd98113304843a339f738647cc13daf8f60312b9fef6b702 |
wormwinDll64 |
e8ecceb0cbc0e6aefab5ac47a9e69f7926317d9e4f9a782b8df418c67a8d0661 |
wormwinDll64 |
Additional Resources
- Hear a comprehensive discussion of today’s top cyberthreats by CrowdStrike experts: register for a webinar on the 2020 Global Threat Report.
- Read a report on CrowdStrike Falcon® Intelligence Automated Threat Intelligence and learn why actionable threat intelligence is the next step in SOC evolution.
- Learn more about comprehensive endpoint protection with the CrowdStrike Falcon® platform by visiting the product page.
- Test CrowdStrike next-gen AV for yourself. Start your free trial of Falcon Prevent™ today.


