Leftover Lunch: Finding, Hunting and Eradicating Spicy Hot Pot, a Persistent Browser Hijacking Rootkit

In this blog, we take a look at a recent incident that involved a persistent browser hijacking rootkit dubbed “Spicy Hot Pot.” The name comes from Huorong (Tinder) Security, which first publicly reported on its discovery of this rootkit. Spicy Hot Pot is a browser hijacking rootkit that changes a user’s homepage to point to a page controlled by the malware operator, in addition to uploading memory dumps from a machine to a predefined server and incorporating a local update feature to ensure it can remain updated. Usually a browser hijacker would do this through malicious executables or registry keys that change the user’s homepage; however, Spicy Hot Pot takes this one step further by using two kernel-mode drivers that are dropped to disk and installed during the infection process to remain stealthy.
These kernel drivers have a number of functions, such as hindering security software by intercepting their callback functions, collecting any memory dumps created on the system from a specific directory, and giving the malware operator the ability to update the malware as they see fit. In addition, one of the kernel drivers acts as a minifilter, which gives it the ability to intercept and modify any user input or output requests. One of the functions of this driver is to intercept any attempts by a user to display the malicious files, effectively making them invisible.
This particular piece of malware is primarily focused on Chinese users. This is inferred based on 1) it was found dropped from a number of keygen/activation tools used to “crack” or illegitimately activate Microsoft products that are developed with Chinese language packs, and 2) this malware is specifically targeting common antivirus software used in China. Although more can be said about this piece of malware, this blog post aims to give a quick overview of Spicy Hot Pot, its capabilities and how it can be manually removed from a host without the need for third-party software.
The Initial Detection
In June 2020, the CrowdStrike Falcon® Complete™ team received a machine learning (ML) alert that a suspicious binary called “baofeng15.0” attempted to run in a customer’s environment. This had the below SHA256 hash:
-
498ed725195b5ee52e406de237afa9ef268cabc4ef604c363aee2e78b3b13193
After analyzing this binary, the determination was made that it is bundled with a browser hijacking rootkit. This rootkit is known to date back as early as December 2019 and remains prevalent with new variants being discovered to date.
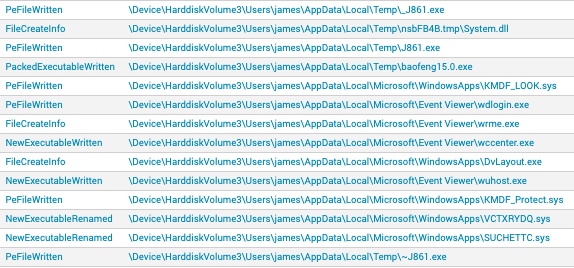
Starting with dynamic analysis of the binary in question, it was revealed that it dropped nine items of interest (seven executables and two filter drivers) before disabling hibernation mode on the machine. A recreation of this activity after disabling preventions can be seen below using CrowdStrike Falcon®’s process execution tree.
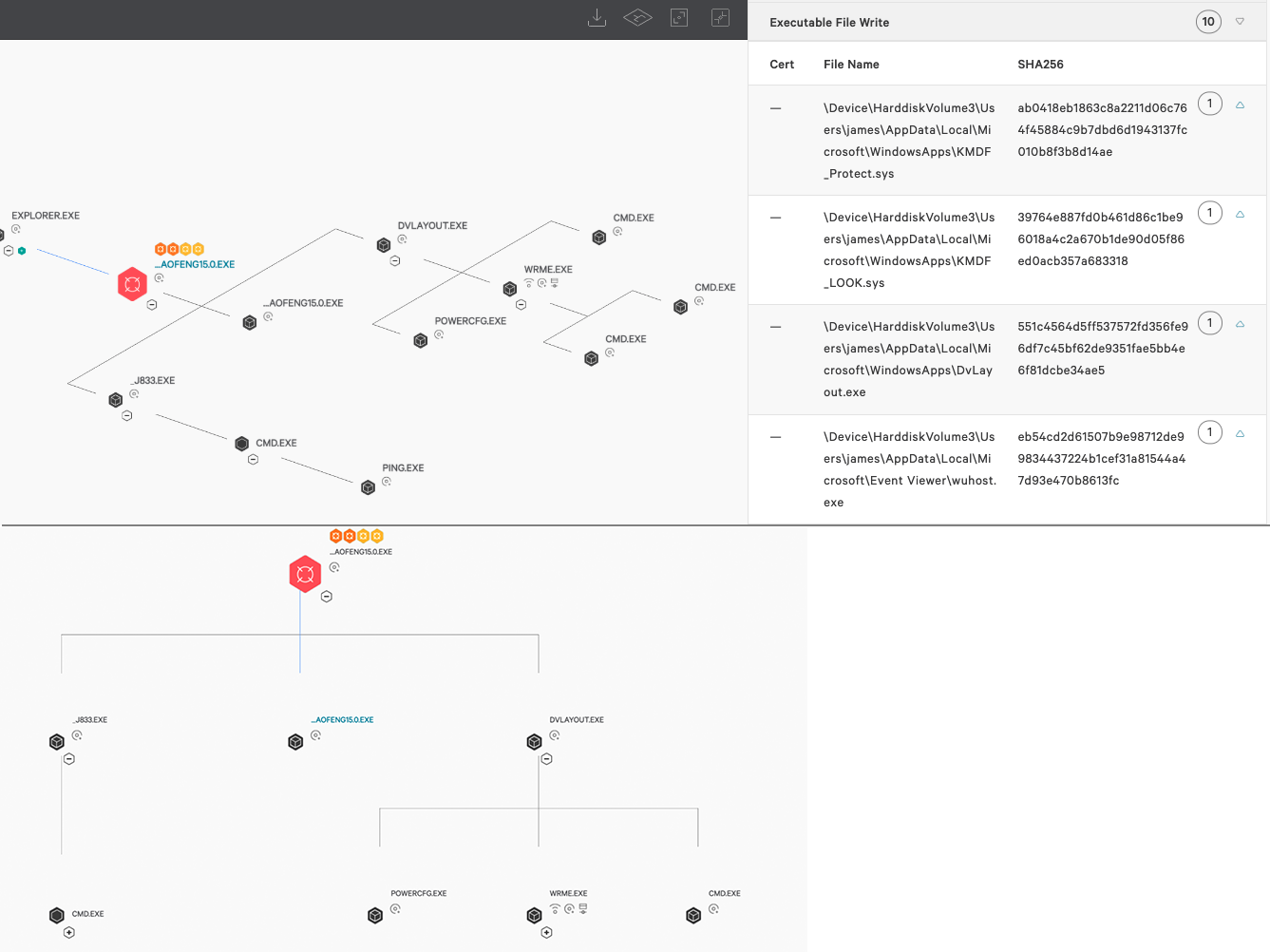
Figure 1. Spicy Hot Pot as seen in the CrowdStrike Falcon® process execution tree (click image to enlarge)
This detection raises a number of questions due to the context and location of dropped binaries when run on a Windows 10 machine.
%localappdata%\Microsoft\Event Viewer\wccenter.exe%localappdata%\Microsoft\Event Viewer\wdlogin.exe%localappdata%\Microsoft\Event Viewer\wrme.exe%localappdata%\Microsoft\Event Viewer\wuhost.exe%localappdata%\Microsoft\WindowsApps\DvLayout.exe%localappdata%\Temp\_J861.exe%localappdata%\Temp\baofeng15.0.exe%localappdata%\Microsoft\WindowsApps\KMDF_LOOK.sys%localappdata%\Microsoft\WindowsApps\KMDF_Protect.sys
On Windows 7, the drivers fall into “Media Player” instead of “WindowsApps.” In addition, this made a number of registry modifications to the local machine’s software hive:
Software\Microsoft\Helicarrier\st\stempSoftware\Microsoft\Helicarrier\ChannelSoftware\Microsoft\DirectX\DvVersionSoftware\Microsoft\DirectX\PvVersionSoftware\Microsoft\DirectX\RvVersionSoftware\Microsoft\Helicarrier\dpSoftware\Microsoft\Helicarrier\caSoftware\Microsoft\Helicarrier\drSoftware\Microsoft\Helicarrier\euSoftware\Microsoft\Helicarrier\fdSoftware\Microsoft\Helicarrier\ap
One important item to note is the presence of a new baofeng15.0.exe binary with a different hash. This was far more widespread than the binary that was just run and had a creation timestamp dating back four years:
2016-01-13 13:19:34
Based on this, it’s likely that an older cracking tool has been repackaged with this malware and distributed online by the malware operator. The other eight files dropped are signed by a few different signing certificates issued to “Beijing JoinHope Image Technology Ltd.” Unique samples found have different validity timeframes for their signing certificates, showing validity issued anywhere from 1 minute to 10 years ago. At the time of writing, all had expired; however, they were still able to be successfully installed due to exceptions to driver signing enforcement.
| File Name | Signing Certificate |
DvLayout.exe |
Valid From 12:00 AM 05/16/2014 Valid To 11:59 PM 05/16/2015 |
wccenter.exe |
Valid From 12:00 AM 05/16/2014 Valid To 11:59 PM 05/16/2015 |
wrme.exe |
Valid From 12:00 AM 02/08/2010 Valid To 11:59 PM 02/07/2020 |
wuhost.exe |
Valid From 12:00 AM 02/08/2010 Valid To 11:59 PM 02/07/2020 |
wdlogin.exe |
Valid From 04:23 AM 08/22/2020
Valid To 04:23 AM 08/22/2020 |
_J861.exe |
Valid From 12:00 AM 02/08/2010 Valid To 11:59 PM 02/07/2020 |
baofeng15.0.exe |
Not Signed |
KMDF_LOOK.sys |
Valid From 02:21 AM 06/13/2020 Valid To 02:21 AM 06/13/2020 |
KMDF_Protect.sys |
Valid From 12:00 AM 05/16/2014 Valid To 11:59 PM 05/16/2015 |
Table 1. Validity timeframes for the files dropped by Spicy Hot Pot
Comparing this signing certificate to a public repository of malware samples reveals hundreds of unique malware samples, indicating that the creator of this malware (or someone with access to these signing certificates) is in no rush to stop using certificates issued to this entity. Many pieces of malware signed by this entity contained similar debugging (pdb) locations in their debug strings.
| Binary | PDB |
KMDF_LOOK.sys |
G:\SVN\源码\驱动\LookFile\KMDF_LOOK\Release\KMDF_LOOK_64.pdb |
KMDF_Protect.sys |
G:\SVN\源码\驱动\protect\KMDF_Protect\Release\KMDF_Protect_64.pdb |
wdlogin.exe |
D:\Work\Install_Driver\Driver_helper\Release\wdlogin.pdb |
wrme.exe |
D:\Work\Install_Driver\Driver_helper\Release\wrme.pdb |
wccenter.exe |
D:\Work\Install_Driver\Driver_helper\Release\wccenter.pdb |
_J861.exe |
E:\work\Icon_Report\Release\_service.pdb |
wuhost.exe |
D:\Work\Install_Driver\Driver_helper\Release\wuhost.pdb |
Table 2. Debugging locations found in Spicy Hot Pot malware
To a normal user, the kernel drivers dropped to disk are completely invisible. This is because not only are they renamed and installed on infection, but through their installation they begin to act as a rootkit — and one of the drivers hides the malware files from being shown on disk. This extends to making the executables dropped to disk invisible. We can see the different filtering capabilities of this driver from analyzing pseudo-code of the file KMDF_Protect.sys.
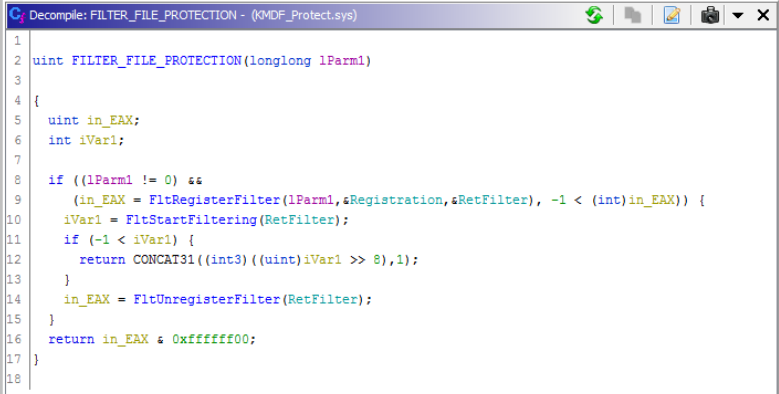
Figure 2. Minifilter being registered
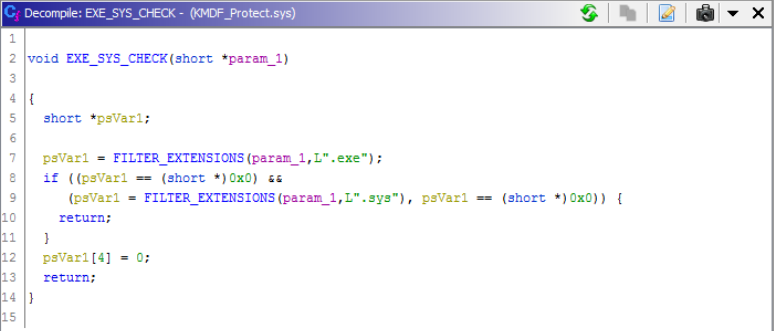
Figure 3. Searching for.sys and .exe files to filter on
In addition to this, KMDF_Protect.sys checks for any executables running with known binary names from Qihoo 360 software.
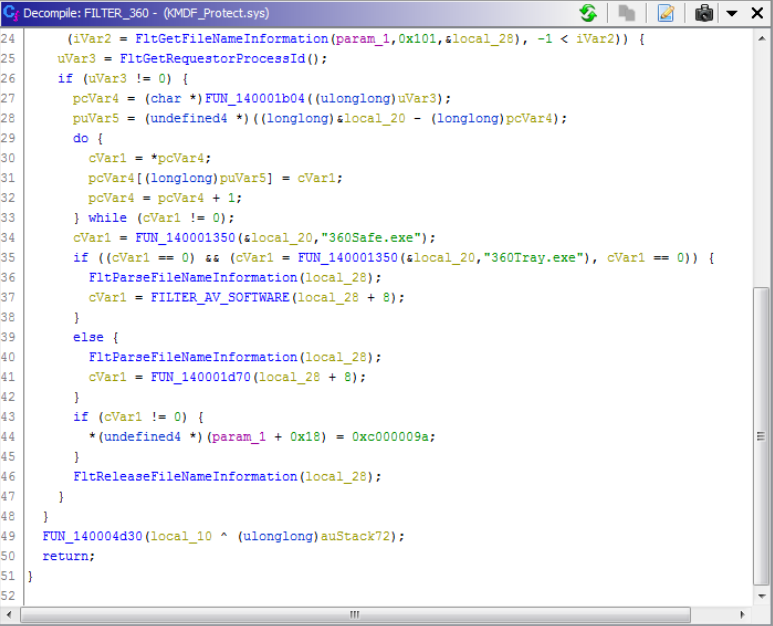
Figure 4. Checking for antivirus software attempting to run
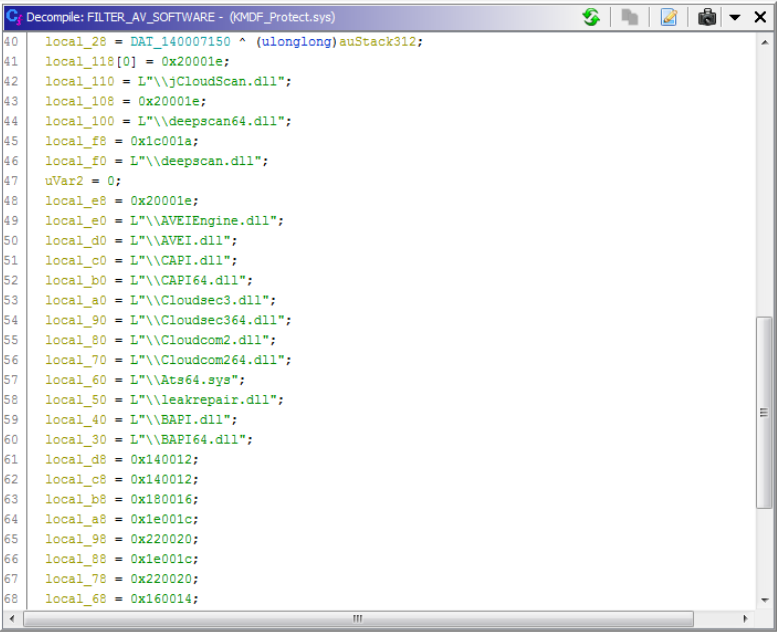
Figure 5. Strings used in preventing antivirus software from loading scanning modules
This also adds a shutdown callback for persistence. At shutdown, the driver attempts to write back the location of wccenter.exe to the system’s “RunOnce” key so that it runs again on boot. As this is performed by the kernel-mode driver, this modification isn’t shown by common registry monitoring tools.
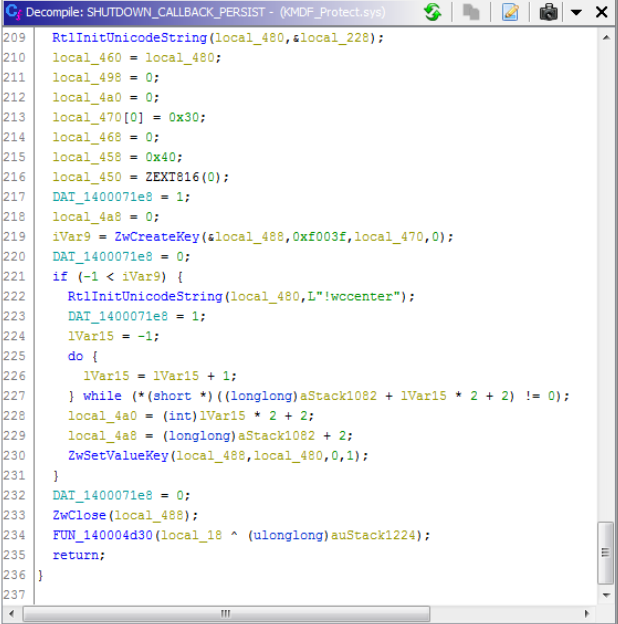
Figure 6. Persistence through a shutdown function callback
If we compare this to KMDF_LOOK.sys, we can see that its primary function is to hijack the user’s homepage and delete process callbacks to security software.
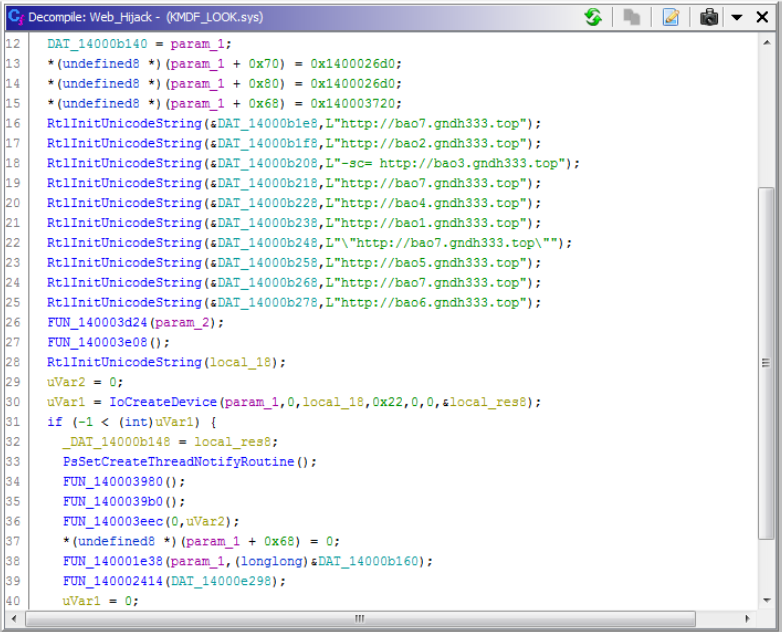
Figure 7. Hardcoded URLs for the browser hijacking component
It should be noted that both drivers masquerade as legitimate service names to remain stealthy:
| Driver | Malicious Service Name | Masqueraded Legitimate Service Name |
KMDF_Protect.sys |
iaLPSS1z | iaLPSSi*: Intel Serial IO Driver |
KMDF_LOOK.sys |
LSI_SAS2l | LSI_SAS2: LSI SAS GEN 2 Driver (StorPort) |
Briefing over other components of this malware:
DVLayout.exeis used to install the rootkit. This creates the Mutex “DVLayout.”_J861.exeis used to gather system information of the infected client, including serial number, and has a number of networking functions that support the operation of this malware. This temporarily creates a service called “R.”wccenter.execommunicates withKMDF_Protect.sysusing a named device created called\\Device\\iaLPSS1zand is used to runwdlogin.exe,wuhost.exeandwrme.exe.
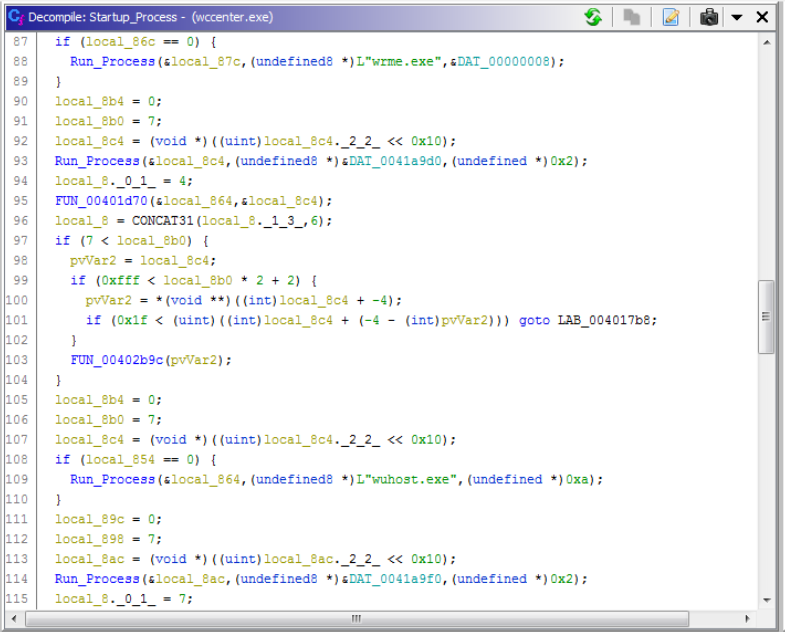
Figure 8. wccenter.exe startup execution
wuhost.exe is used to update the rootkit drivers and modules as required. It creates the Mutex “Update” and contacts one of the following domains to fetch this update:
- https[:]//du[.]testjj[.]com
- https[:]//da[.]testiu[.]com
- https[:]//db[.]testyk[.]com
wrme.exe is used to download and start or install modules such as wuhost.exe and wdlogin.exe in addition to gathering information about the operating system. It creates the Mutex “DLreport.”
wdlogin.exe is used to find any dump file ending with dmp in the %SystemRoot%\minidump directory, compress it, and upload it to one of the above servers at the endpoint /api/v1/post_dump. This is likely for troubleshooting any blue screen errors that may be caused by the rootkit. It creates the Mutex “dumping.”
Investigation with Endpoint Detection and Response Data
Using CrowdStrike Falcon®’s telemetry via our Endpoint Activity Monitoring (EAM) application, we’re able to see the infection actions taking place when protections are disabled. This includes file writes of _J861.exe, KMDF_Protect.sys, KMDF_LOOK.sys, and their associated driver loads.

Figure 10. DriverLoad events as seen in the CrowdStrike Falcon® EAM application (click image to enlarge)
By checking the registry and filter drivers on this host through CrowdStrike Falcon®’s Real Time Response (RTR) capability, we can locate the kernel drivers running and the dropped binaries to prove they reside on disk, given that we know their name and location. This works even though Spicy Hot Pot filters user input and output requests to make the files invisible to a normal user of Windows.
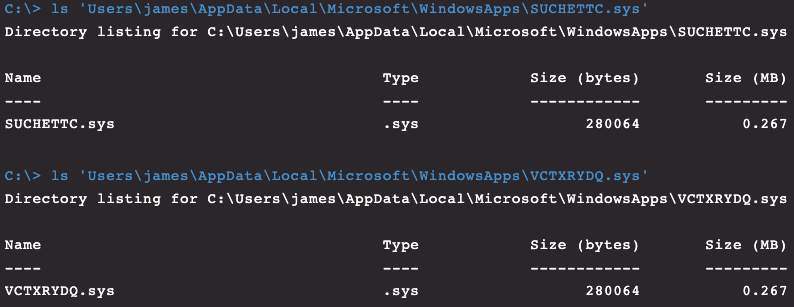
Figure 11. Rootkit drivers as seen through Real Time Response (RTR)
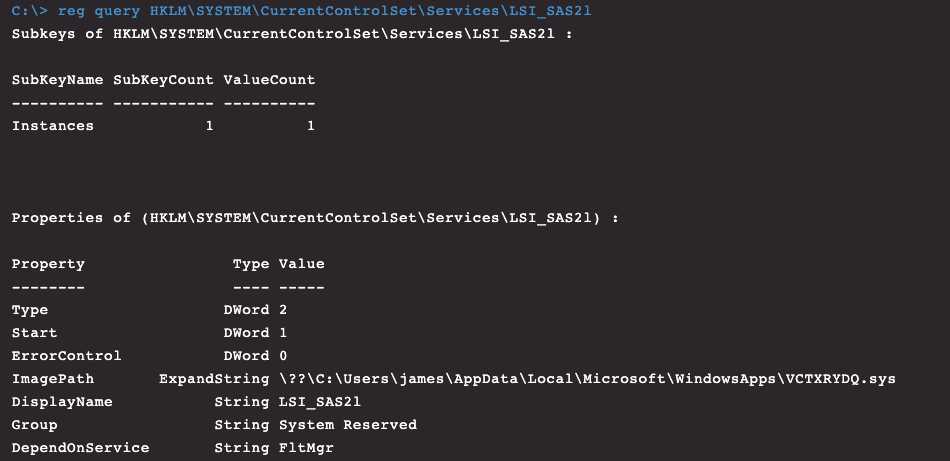
Figure 12. Rootkit service as seen through Real Time Response (RTR)
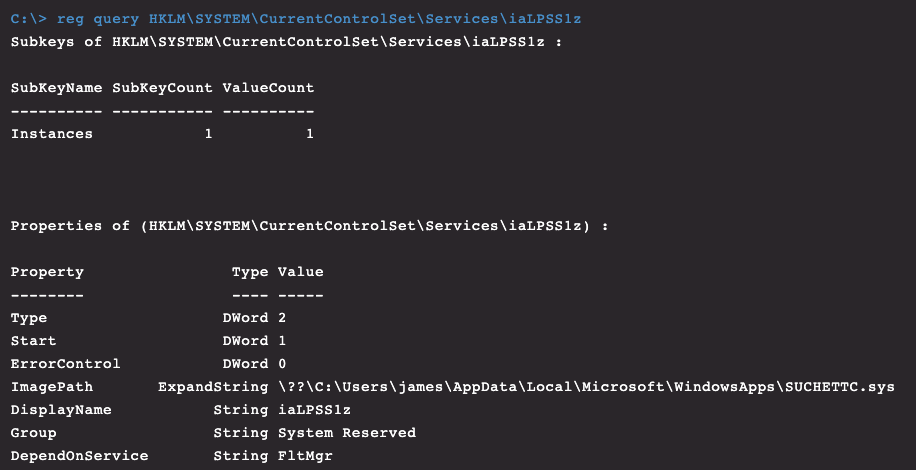 Figure 13. Rootkit service as seen through Real Time Response (RTR)
Figure 13. Rootkit service as seen through Real Time Response (RTR)
The Remediation
Spicy Hot Pot, like many other rootkits, utilizes kernel filter drivers that once started cannot be stopped by a user. These filter drivers prevent removal of registry keys, services or the kernel drivers themselves that are associated with the infection. Due to this, removing Spicy Hot Pot malware remotely can be quite challenging. Remediating a rootkit often requires doing so from a machine that is powered off or booted into safe mode; however, we can remove a rootkit such as Spicy Hot Pot without going to these extremes by making sure it cannot run at startup.
Spicy Hot Pot places the malicious filter drivers within the “WindowsApps” folder, which, in addition to the “Event Viewer” or “Media Player” folder, is what is being filtered on. If you rename the folder, the filter drivers immediately become visible.
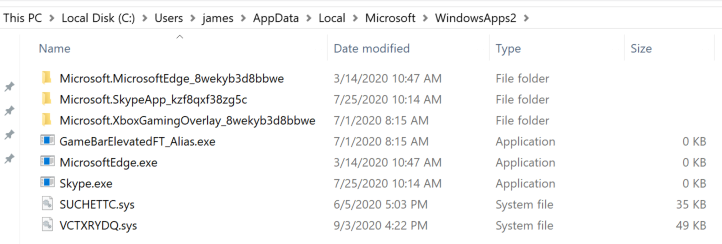
Figure 14. Rootkit drivers visible after renaming WindowsApps folder
This can be done even when the kernel filters are running, but the filter drivers cannot be removed by a user as they’re still running and protected.
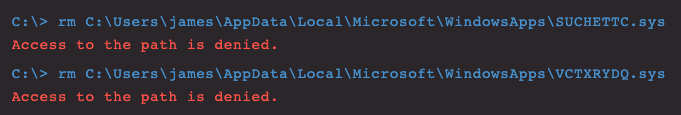
Figure 15. Protected in-use kernel drivers that cannot be removed
After renaming the folder, if you restart an infected system, the path that is referenced by the kernel filter driver services no longer exists, and the drivers will fail to load. At this point, the drivers and associated malicious executables can be removed, and the folder renamed to “WindowsApps” once more. The services and registry keys associated with the rootkit can also be removed now.
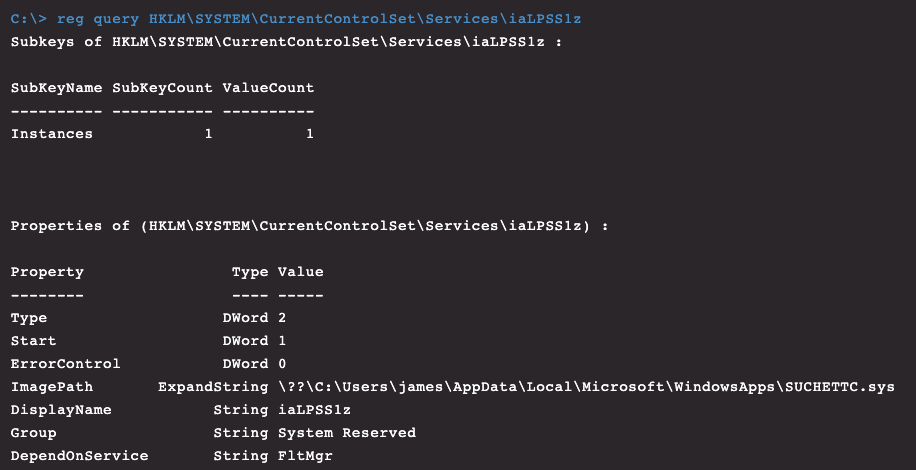
Figure 16. Rootkit driver removal as seen through Real Time Response (RTR)
Conclusion
This post touched on a common browser hijacker being distributed with tools designed to illegitimately activate Microsoft products. It highlights some of the concerns associated with running “cracking” tools on a machine, and why it’s important to monitor and prevent not only unknown executables that are running, but also drivers that are loaded by an operating system and any minifilters present.
By fusing CrowdStrike Falcon®’s detection and prevention capabilities, enriched endpoint telemetry, Real Time Response capability and the expertise of the CrowdStrike Falcon® Complete team, you’re uniquely positioned with the capability to detect, investigate, understand and respond to unknown threats within your environment 24/7, 365 days of the year.
Indicators
| Type | Name/Purpose | Indicator |
| SHA256 | baofeng15.0 | 498ed725195b5ee52e406de237afa9ef268cabc4ef604c363aee2e78b3b13193 |
| SHA256 | DvLayout.exe | 551c4564d5ff537572fd356fe96df7c45bf62de9351fae5bb4e6f81dcbe34ae5 |
| SHA256 | wccenter.exe | 17095beda4afeabb7f41ff07cf866ddc42e49da1a4ed64b9c279072caab354f6 |
| SHA256 | wrme.exe | 7e489f1f72cac9f1c88bdc6be554c78b5a14197d63d1bae7e41de638e903af21 |
| SHA256 | wuhost.exe | eb54cd2d61507b9e98712de99834437224b1cef31a81544a47d93e470b8613fc |
| SHA256 | wdlogin.exe | 7c0fdee3670cc53a22844d691307570a21ae3be3ce4b66e46bb6d9baad1774b8 |
| SHA256 | _J861.exe | c83e6b96ee3aa1a580157547eae88d112d2202d710218f2ed496f7fe3d861abc |
| SHA256 | baofeng15.0.exe | c5802c7fbad5cdf257bcc0f71e8b1c8853e06da411133b5dc78bd6c891f27500 |
| SHA256 | KMDF_LOOK.sys | 39764e887fd0b461d86c1be96018a4c2a670b1de90d05f86ed0acb357a683318 |
| SHA256 | KMDF_Protect.sys | ab0418eb1863c8a2211d06c764f45884c9b7dbd6d1943137fc010b8f3b8d14ae |
| Domain | Update/C2 | du[.]testjj[.]com |
| Domain | Update/C2 | da[.]testiu[.]com |
| Domain | Update/C2 | db[.]testyk[.]com |
| Domain | Hijacking Domain | gndh333[.]top |
| Mutex | wrme.exe | DLreport |
| Mutex | wdlogin | dumping |
| Mutex | wuhost | Update |
| Mutex | DVLayout | DVLayout |
MITRE ATT&CK® Mapping
| Tactic | Technique | Sub-Technique | ID |
| Reconnaissance | Search Open Websites/Domains | Search Engines | T1593.002 |
| Resource Development | Acquire Infrastructure | Domains | T1583.001 |
| Resource Development | Obtain Capabilities | Digital Certificates | T1588.004 |
| Initial Access | Supply Chain Compromise | Compromise Software Supply Chain | T1195.002 |
| Persistence | Boot or Logon Autostart Execution | Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder | T1547.001 |
| Persistence | Create or Modify System Process | Windows Service | T1543.003 |
| Defense Evasion | Rootkit | – | T1014 |
| Defense Evasion | Impair Defenses | Disable or Modify Tools | T1562.001 |
| Defense Evasion | Masquerading | Invalid Code Signature | T1036.001 |
| Defense Evasion | Masquerading | Masquerade Task or Service | T1036.004 |
| Defense Evasion | Masquerading | Match Legitimate Name or Location | T1036.005 |
| Collection | Automated Collection | – | T1119 |
| Command and Control | Encrypted Channel | Asymmetric Cryptography | T1573.002 |
| Exfiltration | Automated Exfiltration | – | T1020 |
| Exfiltration | Exfiltration Over C2 Channel | – | T1041 |
| Impact | Defacement | Internal Defacement | T1491.001 |
| Impact | Service Stop | – | T1489 |
Yara Rules
| /*
YARA Rule Set
|
Additional Resources
- Learn more by visiting the Falcon Complete product webpage.
- Read a white paper: CrowdStrike Falcon® Complete: Instant Cybersecurity Maturity for Organizations of All Sizes.
- Test CrowdStrike next-gen AV for yourself: Start your free trial of Falcon Prevent™.